Observability for Databricks Models with Langfuse
Databricks provides a powerful platform for hosting and serving large language models. By combining Databricks’ serving endpoints with Langfuse, you can trace, monitor, and analyze your AI workloads in development and production.
This notebook demonstrates three different ways to use Databricks models with Langfuse:
- OpenAI SDK: Use Databricks model endpoints via the OpenAI SDK.
- LangChain: Integrate with the Databricks LLM interface in a LangChain pipeline.
- LlamaIndex: Use Databricks endpoints within LlamaIndex.
What is Databricks Model Serving?
Databricks Model Serving allows you to serve large-scale models in a production environment, with automatic scaling and a robust infrastructure. It also enables you to fine-tune LLMs on your private data, ensuring your models can leverage proprietary information while maintaining data privacy.
What is Langfuse?
Langfuse is an open source platform for LLM observability and monitoring. It helps you trace and monitor your AI applications by capturing metadata, prompt details, token usage, latency, and more.
1. Install Dependencies
Before you begin, install the necessary packages in your Python environment:
- openai: Needed to call Databricks endpoints via the OpenAI SDK.
- databricks-langchain: Needed to call Databricks endpoints via an “OpenAI-like” interface.
- llama-index and llama-index-llms-databricks: For using Databricks endpoints within LlamaIndex.
- langfuse: Required for sending trace data to the Langfuse platform.
%pip install openai langfuse databricks-langchain llama-index llama-index-llms-databricks openinference-instrumentation-llama-index2. Set Up Environment Variables
Configure your Langfuse credentials and Databricks credentials as environment variables. Replace the dummy keys below with the real ones from your respective accounts.
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY/LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY: From your Langfuse Project Settings.LANGFUSE_BASE_URL:https://cloud.langfuse.com(EU region) orhttps://us.cloud.langfuse.com(US region).DATABRICKS_TOKEN: Your Databricks personal access token.DATABRICKS_HOST: Your Databricks workspace URL (e.g.,https://dbc-xxxxxxx.cloud.databricks.com).
import os
# Example environment variables (replace with your actual keys/tokens)
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..." # your public key
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..." # your secret key
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # or https://us.cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["DATABRICKS_TOKEN"] = "dapi-..." # Databricks personal access token
os.environ["DATABRICKS_HOST"] = "https://dbc-XXXXX-XXXX.cloud.databricks.com"Approach 1: Using Databricks Models via the OpenAI SDK
Databricks endpoints can act as a drop-in replacement for the OpenAI API. This makes it easy to integrate with existing code that relies on the openai library. Under the hood, langfuse.openai.OpenAI automatically traces your requests to Langfuse.
Steps
- Import the
OpenAIclient fromlangfuse.openai. - Create a client, setting
api_keyto your Databricks token andbase_urlto your Databricks workspace endpoints. - Use the client’s
chat.completions.create()method to send a prompt. - See the trace in your Langfuse dashboard.
Note: For more examples on tracing OpenAI with Langfuse see the OpenAI integration docs.
# Langfuse OpenAI client
from langfuse.openai import OpenAI
# Retrieve the environment variables
databricks_token = os.environ.get("DATABRICKS_TOKEN")
databricks_host = os.environ.get("DATABRICKS_HOST")
# Create an OpenAI-like client pointing to Databricks
client = OpenAI(
api_key=databricks_token, # Databricks personal access token
base_url=f"{databricks_host}/serving-endpoints", # your Databricks workspace
)response = client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an AI assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What is Databricks?"}
],
model="mistral-7b", # Adjust based on your Databricks serving endpoint name
max_tokens=256
)
# Print out the response from the model
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Once the request completes, log in to your Langfuse dashboard and look for the new trace. You will see details like the prompt, response, latency, token usage, etc.

Link to public trace in Langfuse
Approach 2: Using LangChain
Databricks models can also be used via LangChain. The ChatDatabricks class wraps your Databricks Model Serving endpoint.
Steps
- Set
DATABRICKS_HOSTas an environment variable. - Initialize a Langfuse
CallbackHandlerthat automatically collects trace data. - Use
ChatDatabrickswith your endpoint name, temperature, or other parameters. - Invoke the model with messages and pass in the Langfuse callback handler.
- See the trace in your Langfuse dashboard.
Note: For more examples on tracing LangChain with Langfuse see the LangChain integration docs.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
# Initialize Langfuse CallbackHandler for Langchain (tracing)
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()from databricks_langchain import ChatDatabricks
chat_model = ChatDatabricks(
endpoint="mistral-7b", # Your Databricks Model Serving endpoint name
temperature=0.1,
max_tokens=256,
# Other parameters can be added here
)
# Build a prompt as a list of system/user messages
messages = [
("system", "You are a chatbot that can answer questions about Databricks."),
("user", "What is Databricks Model Serving?")
]
# Invoke the model using LangChain's .invoke() method
chat_model.invoke(messages, config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})After running the code, open your Langfuse dashboard to see the recorded conversation.
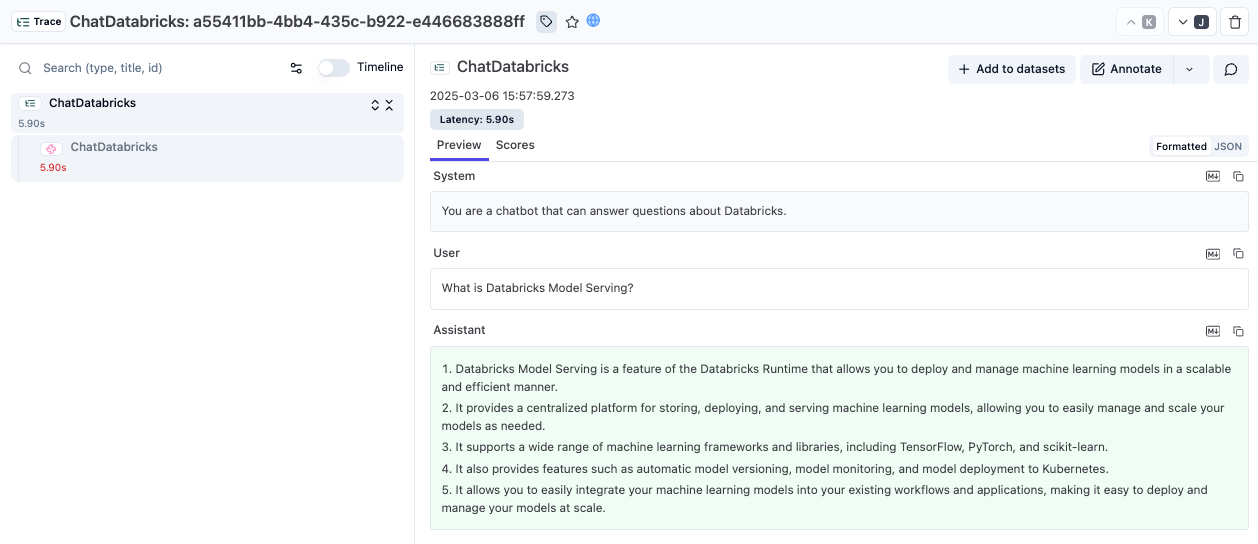
Link to public trace in Langfuse
Approach 3: Using LlamaIndex
If you use LlamaIndex for data ingestion, indexing, or retrieval-augmented generation, you can replace the default LLM with a Databricks endpoint.
Steps
- Import
Databricksfromllama_index.llms.databricks. - Initialize a
DatabricksLLM with your endpoint name and Databricks credentials. - Use
LlamaIndexInstrumentorfromlangfuse.llama_indexto enable automatic tracing. - Invoke the LLM with a chat request.
- See the trace in your Langfuse dashboard.
Note: For more examples on tracing LlamaIndex with Langfuse see the LlamaIndex integration docs.
from llama_index.llms.databricks import Databricks
# Create a Databricks LLM instance
llm = Databricks(
model="mistral-7b", # Your Databricks serving endpoint name
api_key=os.environ.get("DATABRICKS_TOKEN"),
api_base=f"{os.environ.get('DATABRICKS_HOST')}/serving-endpoints/"
)import os
from langfuse import get_client
from openinference.instrumentation.llama_index import LlamaIndexInstrumentor
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
langfuse = get_client()
# Initialize LlamaIndex instrumentation
LlamaIndexInstrumentor().instrument()from llama_index.core.llms import ChatMessage
messages = [
ChatMessage(role="system", content="You are a helpful assistant."),
ChatMessage(role="user", content="What is Databricks?")
]
response = llm.chat(messages)
print(response)You can now log into Langfuse to view your LlamaIndex calls, with details on prompts, token usage, completion data, and more.
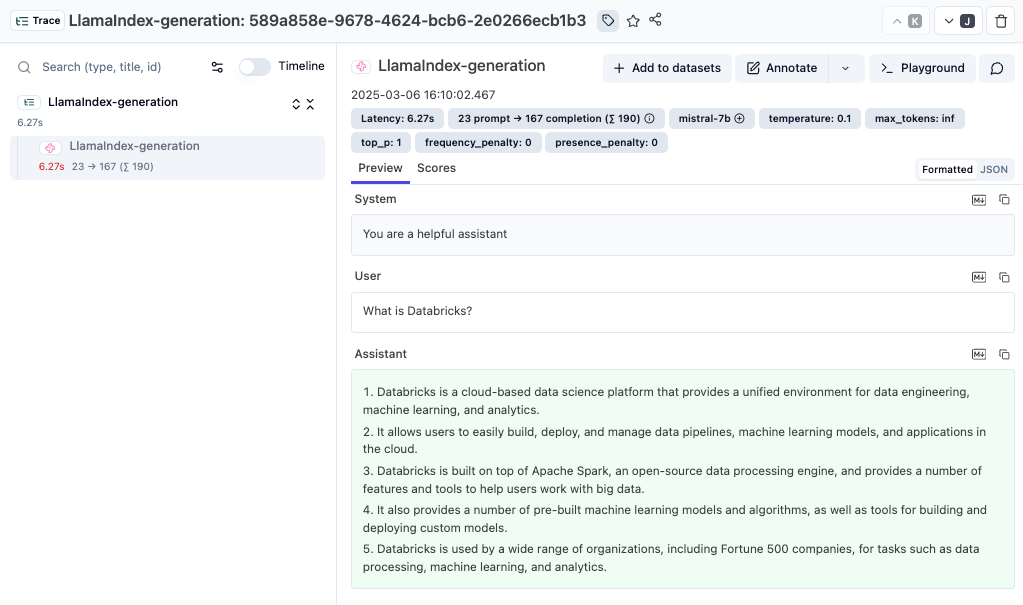
Link to public trace in Langfuse
Interoperability with the Python SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse SDKs to add additional attributes to the trace.
The @observe() decorator provides a convenient way to automatically wrap your instrumented code and add additional attributes to the trace.
from langfuse import observe, propagate_attributes, get_client
langfuse = get_client()
@observe()
def my_llm_pipeline(input):
# Add additional attributes (user_id, session_id, metadata, version, tags) to all spans created within this execution scope
with propagate_attributes(
user_id="user_123",
session_id="session_abc",
tags=["agent", "my-trace"],
metadata={"email": "user@langfuse.com"},
version="1.0.0"
):
# YOUR APPLICATION CODE HERE
result = call_llm(input)
# Update the trace input and output
langfuse.update_current_trace(
input=input,
output=result,
)
return resultLearn more about using the Decorator in the Langfuse SDK instrumentation docs.
Troubleshooting
No traces appearing
First, enable debug mode in the Python SDK:
export LANGFUSE_DEBUG="True"Then run your application and check the debug logs:
- OTel spans appear in the logs: Your application is instrumented correctly but traces are not reaching Langfuse. To resolve this:
- Call
langfuse.flush()at the end of your application to ensure all traces are exported. - Verify that you are using the correct API keys and base URL.
- Call
- No OTel spans in the logs: Your application is not instrumented correctly. Make sure the instrumentation runs before your application code.
Unwanted observations in Langfuse
The Langfuse SDK is based on OpenTelemetry. Other libraries in your application may emit OTel spans that are not relevant to you. These still count toward your billable units, so you should filter them out. See Unwanted spans in Langfuse for details.
Missing attributes
Some attributes may be stored in the metadata object of the observation rather than being mapped to the Langfuse data model. If a mapping or integration does not work as expected, please raise an issue on GitHub.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application:
Interoperability with the Python SDK
- See how to use Databricks models in the Langfuse Playground and for LLM-as-a-Judge evaluations here.
- Explore the Databricks documentation for advanced model serving configurations.
- Learn more about Langfuse tracing features to track your entire application flow.
- Try out Langfuse Prompt Management or set up LLM-as-a-Judge evaluations.