LangChain Tracing & LangGraph Integration
Langfuse integrates with LangChain using LangChain Callbacks — the standard mechanism for hooking into the execution of LangChain components. The Langfuse CallbackHandler automatically captures detailed traces of your LangChain executions, LLMs, tools, and retrievers to evaluate and debug your application.
What is LangChain? LangChain is an open-source framework that helps developers build applications powered by large language models (LLMs) by providing tools to connect models with external data, APIs, and logic.
What is LangGraph? LangGraph is a framework built on top of LangChain that makes it easier to design and run stateful, multi-step AI agents using a graph-based architecture.
What is Langfuse? Langfuse is a platform for observability and tracing of LLM applications. It captures everything happening during an LLM interaction: inputs, outputs, tool usage, retries, latencies and costs and allows you to evaluate and debug your application.
Getting Started
Install Dependencies
pip install langfuse langchain langchain_openai langgraphInitialize Langfuse Callback Handler
Next, set up your Langfuse API keys. You can get these keys by signing up for a free Langfuse Cloud account or by self-hosting Langfuse. These environment variables are essential for the Langfuse client to authenticate and send data to your Langfuse project.
LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY = "sk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY = "pk-lf-..."
LANGFUSE_BASE_URL = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# LANGFUSE_BASE_URL = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
OPENAI_API_KEY = "sk-proj-..."With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse Client and the CallbackHandler. You can also use constructor arguments to initialize the Langfuse client.
from langfuse import get_client
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
# Initialize Langfuse client
langfuse = get_client()
# Initialize Langfuse CallbackHandler for Langchain (tracing)
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()LangChain Example
Instrumenting LangGraph follows the same pattern. Simply pass the langfuse_handler to the agent invocation. (Example Notebook).
from langchain.agents import create_agent
def add_numbers(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""Add two numbers together and return the result."""
return a + b
agent = create_agent(
model="openai:gpt-5-mini",
tools=[add_numbers],
system_prompt="You are a helpful math tutor who can do calculations using the provided tools.",
)
# Run the agent
agent.invoke(
{"messages": [{"role": "user", "content": "what is 42 + 58?"}]},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}
)See Traces in Langfuse
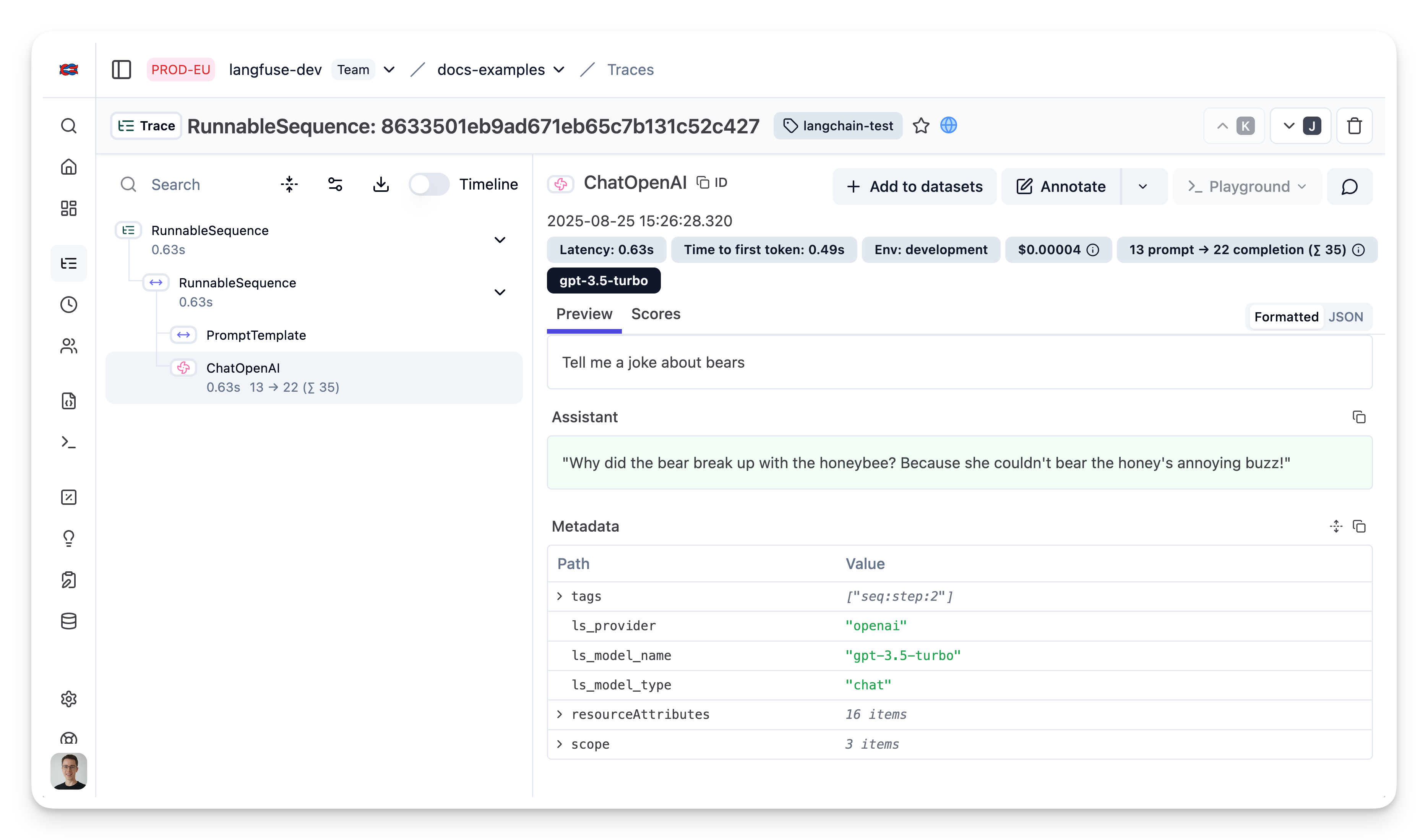
After executing the application, navigate to your Langfuse Trace Table. You will find detailed traces of the application’s execution, providing insights into the LLM calls, retrieval operations, inputs, outputs, and performance metrics.

Example Notebooks
Additional Configuration
Interoperability with Langfuse SDKs
The Langchain integration works seamlessly with the Langfuse SDK to create comprehensive traces that combine Langchain operations with other application logic.
Common use cases:
- Add non-Langchain related observations to the trace
- Group multiple Langchain runs into a single trace
- Set trace-level attributes (
user_id,session_id,tags, etc.)
Using the @observe() decorator:
from langfuse import observe, get_client, propagate_attributes
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
@observe() # Automatically log function as a trace to Langfuse
def process_user_query(user_input: str):
langfuse = get_client()
# Propagate trace attributes to all child observations
with propagate_attributes(
session_id="session-1234",
user_id="user-5678",
):
# Initialize the Langfuse handler - automatically inherits the current trace context
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
# Your Langchain code - will be nested under the @observe trace
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Respond to: {input}")
chain = prompt | llm
result = chain.invoke({"input": user_input}, config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]})
# Update trace with input and final output
langfuse.update_current_trace(
name="user-query-processing",
input={"query": user_input},
output={"response": result.content},
)
return result.content
# Usage
answer = process_user_query("What is the capital of France?")See the Langchain + decorator observability cookbook for an example of this in action.
Using context managers:
from langfuse import get_client, propagate_attributes
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
langfuse = get_client()
# Create a trace via Langfuse spans and use Langchain within it
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(as_type="span", name="multi-step-process") as root_span:
# Update trace attributes
with propagate_attributes(
session_id="session-1234",
user_id="user-5678",
):
# Initialize the Langfuse handler
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
# Step 1: Initial processing (custom logic)
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(as_type="span", name="input-preprocessing") as prep_span:
processed_input = "Simplified: Explain quantum computing"
prep_span.update(output={"processed_query": processed_input})
# Step 2: LangChain processing
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Answer this question: {input}")
chain = prompt | llm
result = chain.invoke(
{"input": processed_input},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}
)
# Step 3: Post-processing (custom logic)
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(as_type="span", name="output-postprocessing") as post_span:
final_result = f"Response: {result.content}"
post_span.update(output={"final_response": final_result})
# Update trace output
root_span.update_trace(
input={"user_query": "Explain quantum computing"},
output={"final_answer": final_result}
)Trace Attributes
You can set trace attributes such as user_id, session_id, and tags dynamically for each LangChain execution.
With Python SDK, you have two options to set trace attributes dynamically:
Option 1: Via metadata fields in chain invocation (simplest approach):
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke about {topic}")
chain = prompt | llm
# Set trace attributes dynamically via metadata
response = chain.invoke(
{"topic": "cats"},
config={
"callbacks": [langfuse_handler],
"metadata": {
"langfuse_user_id": "random-user",
"langfuse_session_id": "random-session",
"langfuse_tags": ["random-tag-1", "random-tag-2"]
}
}
)Option 2: Using the Langfuse SDK
Trace IDs & Distributed Tracing
To pass a custom trace_id to a Langchain execution, you can wrap the execution in a span that sets a predefined trace ID. You can also retrieve the last trace ID a callback handler has created via langfuse_handler.last_trace_id.
from langfuse import get_client, Langfuse
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
langfuse = get_client()
# Generate deterministic trace ID from external system
external_request_id = "req_12345"
predefined_trace_id = Langfuse.create_trace_id(seed=external_request_id)
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler()
# Use the predefined trace ID with trace_context
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(
as_type="span",
name="langchain-request",
trace_context={"trace_id": predefined_trace_id}
) as span:
span.update_trace(
user_id="user_123",
input={"person": "Ada Lovelace"}
)
# LangChain execution will be part of this trace
response = chain.invoke(
{"person": "Ada Lovelace"},
config={"callbacks": [langfuse_handler]}
)
span.update_trace(output={"response": response})
print(f"Trace ID: {predefined_trace_id}") # Use this for scoring later
print(f"Trace ID: {langfuse_handler.last_trace_id}") # Care needed in concurrent environments where handler is reusedScore a Trace
There are multiple ways to score a LangChain trace in Langfuse. See Scoring documentation for more details.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Option 1: Use the yielded span object from the context manager
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(
as_type="span",
name="langchain-request",
trace_context={"trace_id": predefined_trace_id}
) as span:
# ... LangChain execution ...
# Score using the span object
span.score_trace(
name="user-feedback",
value=1,
data_type="NUMERIC",
comment="This was correct, thank you"
)
# Option 2: Use langfuse.score_current_trace() if still in context
with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(as_type="span", name="langchain-request") as span:
# ... LangChain execution ...
# Score using current context
langfuse.score_current_trace(
name="user-feedback",
value=1,
data_type="NUMERIC"
)
# Option 3: Use create_score() with trace ID (when outside context)
langfuse.create_score(
trace_id=predefined_trace_id,
name="user-feedback",
value=1,
data_type="NUMERIC",
comment="This was correct, thank you"
)Queuing and flushing
The Langfuse SDKs queue and batch events in the background to reduce the number of network requests and improve overall performance. In a long-running application, this works without any additional configuration.
If you are running a short-lived application, you need to shutdown Langfuse to ensure that all events are flushed before the application exits.
from langfuse import get_client
# Shutdown the underlying singleton instance
get_client().shutdown()If you want to flush events synchronously at a certain point, you can use the flush method. This will wait for all events that are still in the background queue to be sent to the Langfuse API. This is usually discouraged in production environments.
from langfuse import get_client
# Flush the underlying singleton instance
get_client().flush()Serverless environments (JS/TS)
Since Langchain version > 0.3.0, the callbacks on which Langfuse relies have been backgrounded. This means that execution will not wait for the callback to either return before continuing. Prior to 0.3.0, this behavior was the opposite. If you are running code in serverless environments such as Google Cloud Functions, AWS Lambda or Cloudflare Workers you should set your callbacks to be blocking to allow them time to finish or timeout. This can be done either by
- setting the
LANGCHAIN_CALLBACKS_BACKGROUNDenvironment variable to “false” - importing the global
awaitAllCallbacksmethod to ensure all callbacks finish if necessary
Read more about awaiting callbacks here in the Langchain docs.
AWS Bedrock AgentCore
When deploying LangChain applications to AWS Bedrock AgentCore, the runtime’s ADOT (AWS Distro for OpenTelemetry) auto-instrumentation requires OTEL configuration instead of relying solely on the Langfuse callback handler. See Using Langfuse with an Existing OpenTelemetry Setup for configuration details, or the full Amazon Bedrock AgentCore integration guide.
Azure OpenAI model names
Please add the model keyword argument to the AzureOpenAI or AzureChatOpenAI class to have the model name parsed correctly in Langfuse.
from langchain_openai import AzureChatOpenAI
llm = AzureChatOpenAI(
azure_deployment="my-gpt-4o-deployment",
model="gpt-4o",
)Upgrade Paths for Langchain Integration
This doc is a collection of upgrade paths for different versions of the integration. If you want to add the integration to your project, you should start with the latest version and follow the integration guide above.
Langfuse and Langchain are under active development. Thus, we are constantly improving the integration. This means that we sometimes need to make breaking changes to our APIs or need to react to breaking changes in Langchain. We try to keep these to a minimum and to provide clear upgrade paths when we do make them.
Python
JS/TS
Python
From v2.x.x to v3.x.x
Python SDK v3 introduces a completely revised Langfuse core with a new observability API. While the LangChain integration still relies on a CallbackHandler, nearly all ergonomics have changed. The table below highlights the most important breaking changes:
| Topic | v2 | v3 |
|---|---|---|
| Package import | from langfuse.callback import CallbackHandler | from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler |
| Client handling | Multiple instantiated clients | Singleton pattern, access via get_client() |
| Trace/Span context | CallbackHandler optionally accepted root to group runs | Use context managers with langfuse.start_as_current_observation(...) |
| Dynamic trace attrs | Pass via LangChain config (e.g. metadata["langfuse_user_id"]) | Use metadata["langfuse_user_id"] OR span.update_trace(user_id=...) |
| Constructor args | CallbackHandler(sample_rate=..., user_id=...) | No constructor args – use Langfuse client or spans |
Minimal migration example:
# Install latest SDK (>=3.0.0)
pip install --upgrade langfuse
# v2 Code (for reference)
# from langfuse.callback import CallbackHandler
# handler = CallbackHandler()
# chain.invoke({"topic": "cats"}, config={"callbacks": [handler]})
# v3 Code
from langfuse import Langfuse, get_client
from langfuse.langchain import CallbackHandler
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# 1. Create/Configure Langfuse client (once at startup)
Langfuse(
public_key="your-public-key",
secret_key="your-secret-key",
)
# 2. Access singleton instance and create handler
langfuse = get_client()
handler = CallbackHandler()
# 3. Option 1: Use metadata in chain invocation (simplest migration)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o")
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Tell me a joke about {topic}")
chain = prompt | llm
response = chain.invoke(
{"topic": "cats"},
config={
"callbacks": [handler],
"metadata": {"langfuse_user_id": "user_123"}
}
)
# (Optional) Flush events in short-lived scripts
langfuse.flush()- All arguments such as
sample_rateortracing_enabledmust now be provided when constructing the Langfuse client (or via environment variables) – not on the handler. - Functions like
flush()andshutdown()moved to the client instance (get_client().flush()).
From v1.x.x to v2.x.x
The CallbackHandler can be used in multiple invocations of a Langchain chain as shown below.
from langfuse.callback import CallbackHandler
langfuse_handler = CallbackHandler(PUBLIC_KEY, SECRET_KEY)
# Setup Langchain
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
...
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt, callbacks=[langfuse_handler])
# Add Langfuse handler as callback
chain.run(input="<first_user_input>", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])
chain.run(input="<second_user_input>", callbacks=[langfuse_handler])
So far, invoking the chain multiple times would group the observations in one trace.
TRACE
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAi
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAiWe changed this, so that each invocation will end up on its own trace. This allows us to derive the user inputs and outputs to Langchain applications.
TRACE_1
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAi
TRACE_2
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAiIf you still want to group multiple invocations on one trace, you can use the Langfuse SDK combined with the Langchain integration (more details).
from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()
# Get Langchain handler for a trace
trace = langfuse.trace()
langfuse_handler = trace.get_langchain_handler()
# langfuse_handler will use the trace for all invocationsJS/TS
From v2.x.x to v3.x.x
Requires langchain ^0.1.10. Langchain released a new stable version of the Callback Handler interface and this version of the Langfuse SDK implements it. Older versions are no longer supported.
From v1.x.x to v2.x.x
The CallbackHandler can be used in multiple invocations of a Langchain chain as shown below.
import { CallbackHandler } from "@langfuse/langchain";
// create a handler
const langfuseHandler = new CallbackHandler({
publicKey: LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY,
});
import { LLMChain } from "langchain/chains";
// create a chain
const chain = new LLMChain({
llm: model,
prompt,
callbacks: [langfuseHandler],
});
// execute the chain
await chain.call(
{ product: "<user_input_one>" },
{ callbacks: [langfuseHandler] }
);
await chain.call(
{ product: "<user_input_two>" },
{ callbacks: [langfuseHandler] }
);So far, invoking the chain multiple times would group the observations in one trace.
TRACE
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAi
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAiWe changed this, so that each invocation will end up on its own trace. This is a more sensible default setting for most users.
TRACE_1
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAi
TRACE_2
|
|-- SPAN: Retrieval
| |
| |-- SPAN: LLM Chain
| | |
| | |-- GENERATION: ChatOpenAiIf you still want to group multiple invocations on one trace, you can use the Langfuse SDK combined with the Langchain integration (more details).
const trace = langfuse.trace({ id: "special-id" });
// CallbackHandler will use the trace with the id "special-id" for all invocations
const langfuseHandler = new CallbackHandler({ root: trace });FAQ
- How to customize the names of observations within a Langchain trace?
- How to integrate Langfuse with an existing OpenTelemetry setup
- How to integrate Langfuse with an existing Sentry setup
- How to trace the OpenAI Assistants API?
- LangSmith Alternative? Langfuse vs. LangSmith for LLM Observability
- Why do I see HTTP requests or database queries in my Langfuse traces?