Trace BeeAI Agents in Langfuse
This notebook shows how to trace and observe BeeAI Framework applications with Langfuse using OpenTelemetry instrumentation.
What is BeeAI? BeeAI Framework is a comprehensive toolkit, developed by IBM Research, for building intelligent, autonomous agents and multi-agent systems. It provides everything you need to create agents that can reason, take actions, and collaborate to solve complex problems in both Python and TypeScript.
What is Langfuse? Langfuse is an open source platform for LLM observability and monitoring. It helps you trace and monitor your AI applications by capturing metadata, prompt details, token usage, latency, and more.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Before you begin, install the necessary packages in your Python environment:
%pip install beeai-framework langfuse openinference-instrumentation-beeai "beeai-framework[wikipedia]"Step 2: Configure Langfuse SDK
Next, set up your Langfuse API keys. You can get these keys by signing up for a free Langfuse Cloud account or by self-hosting Langfuse. These environment variables are essential for the Langfuse client to authenticate and send data to your Langfuse project.
You will also need to configure your LLM provider credentials. BeeAI Framework supports multiple providers including OpenAI, Ollama, watsonx.ai, and others.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your LLM provider API key (example with OpenAI, adjust for your provider)
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."
# For Ollama (local), no API key needed
# For other providers, set appropriate environment variables
With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
# Initialise Langfuse client and verify connectivity
langfuse = get_client()
assert langfuse.auth_check(), "Langfuse auth failed - check your keys ✋"
Step 3: OpenTelemetry Instrumentation
Use the BeeAIInstrumentor library to wrap BeeAI Framework calls and send OpenTelemetry spans to Langfuse.
from openinference.instrumentation.beeai import BeeAIInstrumentor
BeeAIInstrumentor().instrument()Step 4: Run an Example
import asyncio
from beeai_framework.agents.react import ReActAgent
from beeai_framework.agents.types import AgentExecutionConfig
from beeai_framework.backend.chat import ChatModel
from beeai_framework.backend.types import ChatModelParameters
from beeai_framework.memory import TokenMemory
from beeai_framework.tools.search.wikipedia import WikipediaTool
from beeai_framework.tools.weather.openmeteo import OpenMeteoTool
# Initialize the language model
llm = ChatModel.from_name(
"openai:gpt-4o-mini", # or "ollama:granite3.3:8b" for local Ollama
ChatModelParameters(temperature=0.7),
)
# Create tools for the agent
tools = [
WikipediaTool(),
OpenMeteoTool(),
]
# Create a ReAct agent with memory
agent = ReActAgent(
llm=llm,
tools=tools,
memory=TokenMemory(llm)
)
# Run the agent
async def main():
response = await agent.run(
prompt="I'm planning a trip to Barcelona, Spain. Can you research key attractions and landmarks I should visit, and also tell me what the current weather conditions are like there?",
execution=AgentExecutionConfig(
max_retries_per_step=3,
total_max_retries=10,
max_iterations=5
),
)
print("Agent Response:", response.result.text)
return response
# Run the example
response = await main()
View Traces in Langfuse
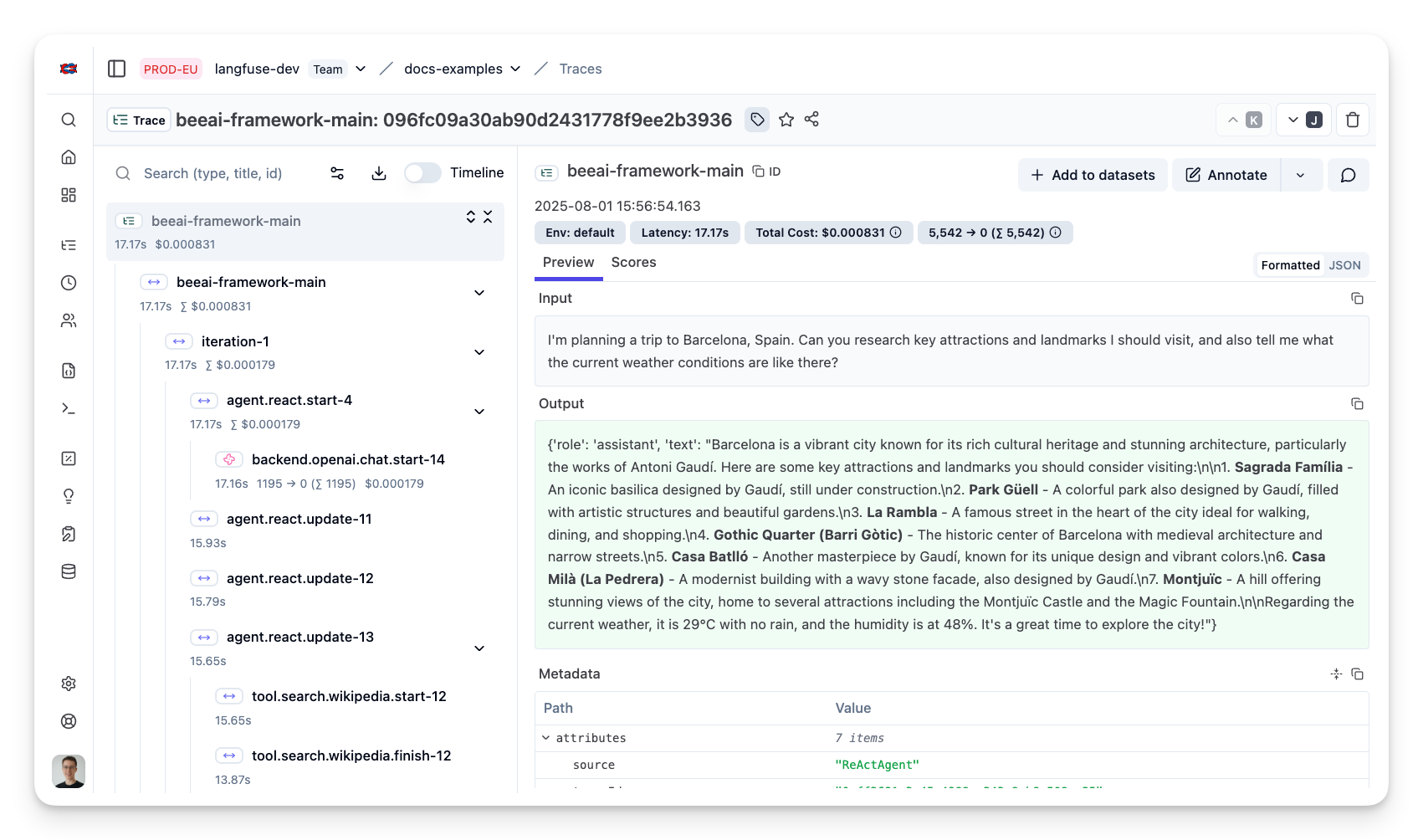
After executing the application, navigate to your Langfuse Trace Table. You will find detailed traces of the application’s execution, providing insights into the agent conversations, tool calls, LLM interactions, inputs, outputs, and performance metrics.
Interoperability with the Python SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse SDKs to add additional attributes to the observation.
The @observe() decorator provides a convenient way to automatically wrap your instrumented code and add additional attributes to the observation.
from langfuse import observe, propagate_attributes, get_client
langfuse = get_client()
@observe()
def my_llm_pipeline(input):
# Add additional attributes (user_id, session_id, metadata, version, tags) to all spans created within this execution scope
with propagate_attributes(
user_id="user_123",
session_id="session_abc",
tags=["agent", "my-observation"],
metadata={"email": "user@langfuse.com"},
version="1.0.0"
):
# YOUR APPLICATION CODE HERE
result = call_llm(input)
return result
# Run the function
my_llm_pipeline("Hi")Learn more about using the Decorator in the Langfuse SDK instrumentation docs.
Troubleshooting
No observations appearing
First, enable debug mode in the Python SDK:
export LANGFUSE_DEBUG="True"Then run your application and check the debug logs:
- OTel observations appear in the logs: Your application is instrumented correctly but observations are not reaching Langfuse. To resolve this:
- Call
langfuse.flush()at the end of your application to ensure all observations are exported. - Verify that you are using the correct API keys and base URL.
- Call
- No OTel spans in the logs: Your application is not instrumented correctly. Make sure the instrumentation runs before your application code.
Unwanted observations in Langfuse
The Langfuse SDK is based on OpenTelemetry. Other libraries in your application may emit OTel spans that are not relevant to you. These still count toward your billable units, so you should filter them out. See Unwanted spans in Langfuse for details.
Missing attributes
Some attributes may be stored in the metadata object of the observation rather than being mapped to the Langfuse data model. If a mapping or integration does not work as expected, please raise an issue on GitHub.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application: