Tracing using the OpenInference SDK
Langfuse offers an OpenTelemetry compatible SDK. With the OpenInference instrumentation library, you can log traces from multiple other frameworks to Langfuse. Below is an example of tracing OpenAI to Langfuse, you can find a full list of supported frameworks here. To make this example work with other frameworks, you just need to change the instrumentor to match the framework.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Install the necessary Python packages to enable OpenTelemetry tracing, openinference instrumentation, and the OpenAI SDK for making LLM requests.
%pip install langfuse openai openinference-instrumentation-openai --upgradeStep 2: Configure Environment Variables
Set your Langfuse API keys for the basic auth header. Get your Langfuse API keys by signing up for Langfuse Cloud or self-hosting Langfuse.
Also, add your OPENAI_API_KEY as an environment variable.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Verify connection
if langfuse.auth_check():
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
else:
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!Step 3: Initialize Instrumentation
We use the OpenAIInstrumentor to instrument the OpenAI SDK. You can replace this with any of the frameworks supported here
from openinference.instrumentation.openai import OpenAIInstrumentor
OpenAIInstrumentor().instrument()Step 4: Execute a Sample LLM Request
With instrumentation enabled, every OpenAI API call will now be traced. The following example sends a chat completion request to illustrate the integration.
import openai
response = openai.OpenAI().chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "How does enhanced LLM observability improve AI debugging?",
}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Enhanced observability in large language models (LLMs) plays a crucial role in improving AI debugging by providing deeper insights into model performance, behavior, and internal mechanics. Here are several ways in which enhanced observability can improve AI debugging:
1. **Detailed Monitoring**: Enhanced observability allows developers to monitor various metrics related to model performance in real time, such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 scores across different tasks. This helps identify specific areas where the model is underperforming.
2. **Data Drift Detection**: Observability tools can monitor incoming data distributions and detect drift over time. If the data the model encounters changes significantly from the training data, this can lead to degraded performance. Detecting data drift enables timely interventions, such as model retraining or adjustment.
3. **Error Analysis**: Enhanced observability tools can assist in logging and categorizing errors made by the model, such as misclassifications or inappropriate responses. By analyzing these errors, developers can pinpoint patterns and root causes, guiding debugging efforts more effectively.
4. **Model Interpretability**: Observability can be coupled with interpretability tools that provide insights into how a model makes decisions. By understanding the features or tokens that lead to certain outputs, developers can identify whether the model is relying on spurious correlations or misjudgments in particular contexts.
5. **Traceability**: With enhanced observability, it's possible to track the inputs and outputs of the model dynamically. This feature can help reproduce issues and understand the circumstances under which certain errors occur, facilitating quicker resolutions.
6. **User Feedback Integration**: Integrating user feedback into observability systems can provide qualitative insights into model performance. When users provide feedback on model outputs, it can highlight areas of misunderstanding or repeated errors that quantitative metrics may not reveal.
7. **Performance Variability Monitoring**: Tracking performance variability across different populations or contexts can uncover biases or inconsistencies in model behavior. By identifying and understanding these variances, developers can address fairness and ethical concerns more efficiently.
8. **Version Control and Experimentation**: Observability can provide a framework for tracking experiments with different model versions. This allows developers to understand how changes in training data, model architecture, or hyperparameters affect performance, making it easier to identify optimal configurations.
9. **Logging Contextual Information**: By capturing contextual information during model execution (e.g., user queries, environmental variables), developers can better understand the conditions that lead to specific outputs, making debugging more straightforward.
10. **Alerts and Anomaly Detection**: With enhanced observability, systems can automatically alert developers to anomalies in performance, enabling them to investigate and resolve issues proactively, rather than reactively waiting for user reports or performance drops.
In conclusion, enhanced observability fosters a more proactive and informed debugging process for large language models. By improving transparency and understanding of the model's behavior, developers can diagnose issues more efficiently, refine model performance, and ultimately build more robust AI solutions.Step 5: View the Traces in Langfuse
After running the above code, you can inspect the generated traces on your Langfuse dashboard:
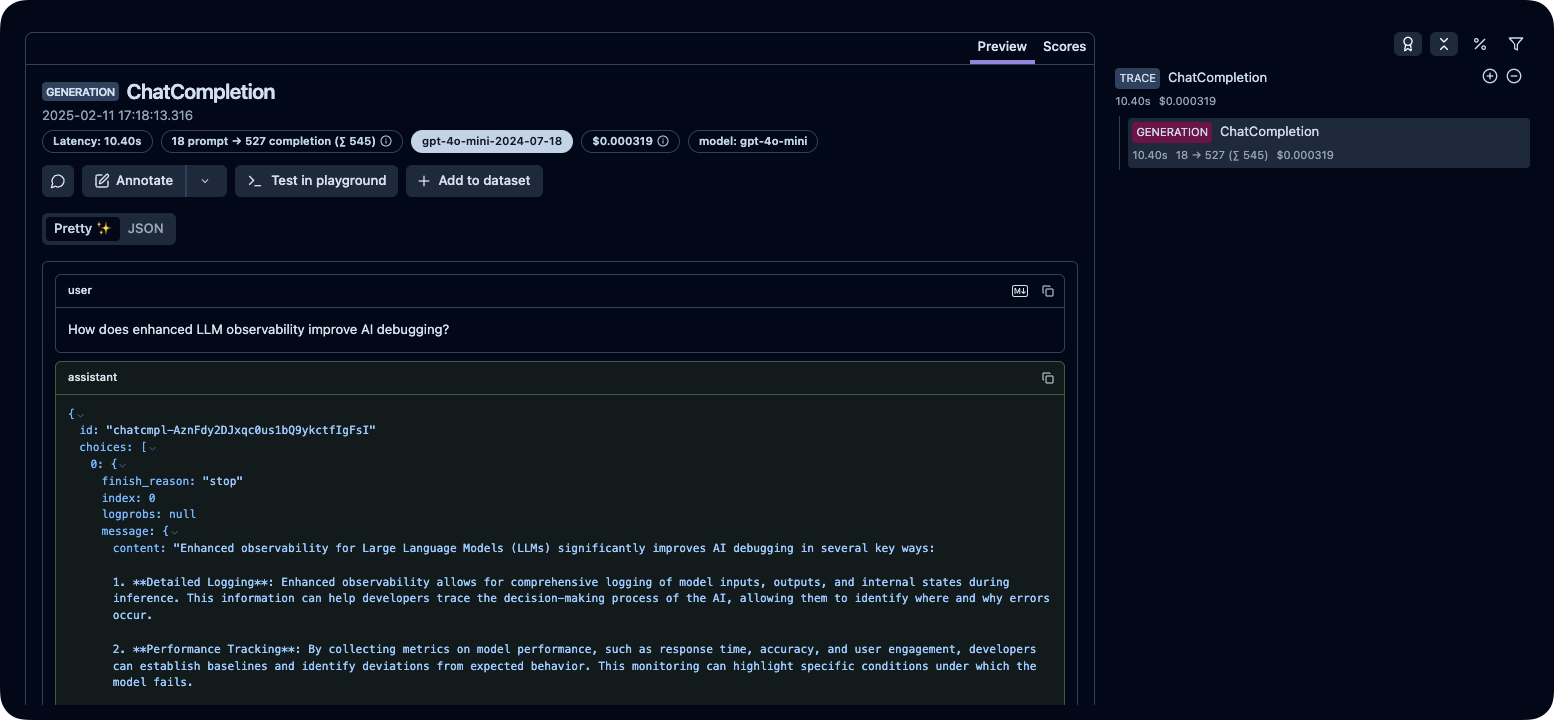
Public example trace in Langfuse