Observability for Novita AI with Langfuse
This guide shows you how to integrate Novita AI with Langfuse. Novita AI’s API endpoints for chat, language and code are fully compatible with OpenAI’s API. This allows us to use the Langfuse OpenAI drop-in replacement to trace all parts of your application.
What is Novita AI? Novita AI is an AI cloud platform that helps developers easily deploy AI models through a simple API, backed by affordable and reliable GPU cloud infrastructure. You can try the Novita AI Llama 3 API Demo here.
What is Langfuse? Langfuse is an open source LLM engineering platform that helps teams trace API calls, monitor performance, and debug issues in their AI applications.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Make sure you have installed the necessary Python packages:
%pip install openai langfuseStep 2: Set Up Environment Variables
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page
# https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Get your Novita AI API key from the project settings page
os.environ["NOVITA_API_KEY"] = "..."Step 3: Langfuse OpenAI drop-in Replacement
In this step we use the native OpenAI drop-in replacement by importing from langfuse.openai import openai.
To start using Novita AI with OpenAI’s client libraries, pass in your Novita AI API key to the api_key option, and change the base_url to https://api.novita.ai/v3/openai:
# instead of import openai:
from langfuse.openai import openai
client = openai.OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ.get("NOVITA_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.novita.ai/v3/openai",
)Note: The OpenAI drop-in replacement is fully compatible with the Low-Level Langfuse Python SDKs and @observe() decorator to trace all parts of your application.
Step 4: Run An Example
The following cell demonstrates how to call Novita AI’s chat model using the traced OpenAI client. All API calls will be automatically traced by Langfuse.
client = openai.OpenAI(
api_key=os.environ.get("NOVITA_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.novita.ai/v3/openai",
)
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="meta-llama/llama-3.1-70b-instruct",
messages=[
{"role": "system", "content": "Act like you are a helpful assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "What are the famous attractions in San Francisco?"},
]
)
print(response.choices[0].message.content)Step 5: See Traces in Langfuse
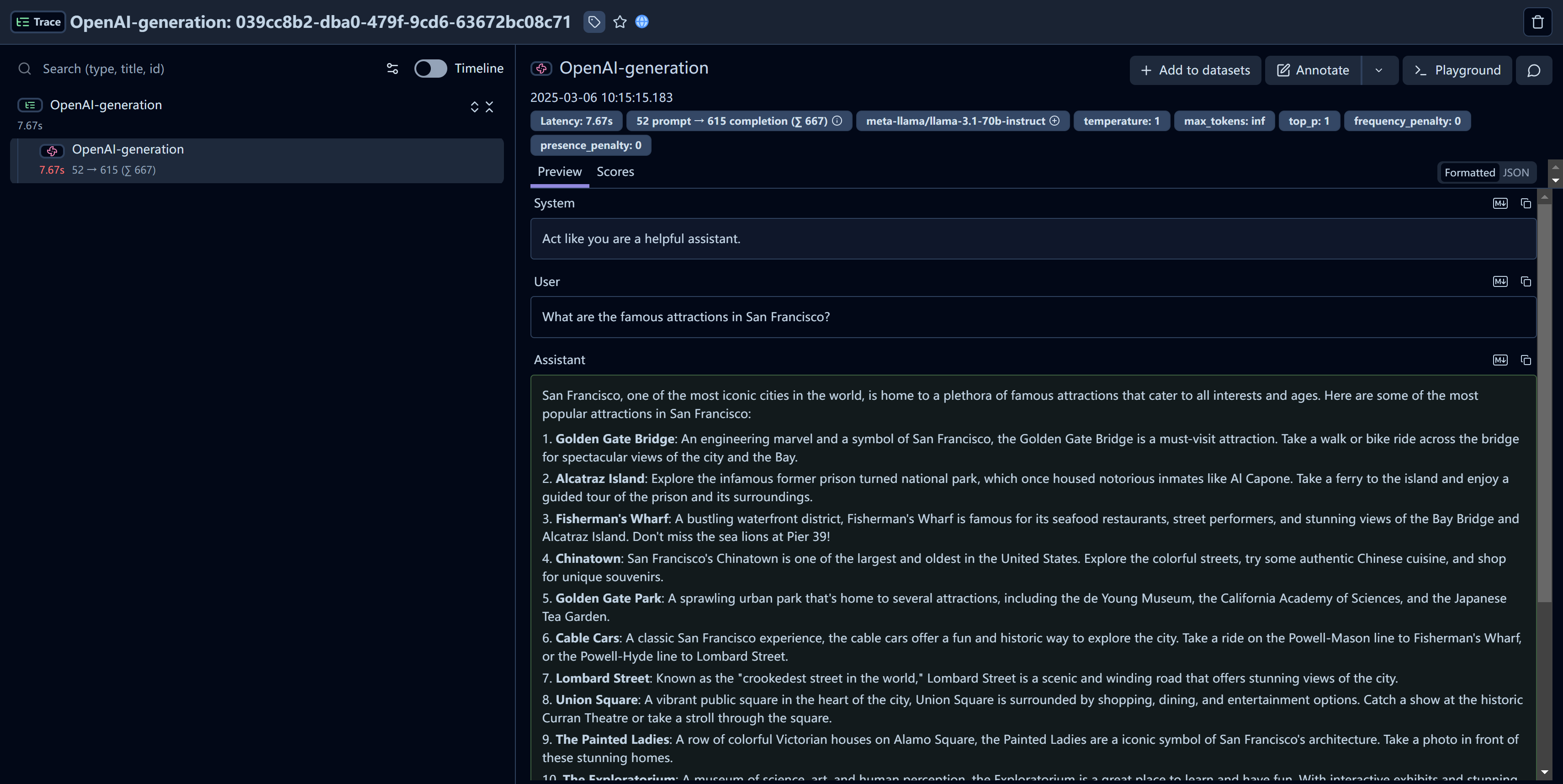
After running the example model call, you can see the traces in Langfuse. You will see detailed information about your Novita AI API calls, including:
- Request parameters (model, messages, temperature, etc.)
- Response content
- Token usage statistics
- Latency metrics
Interoperability with the Python SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse SDKs to add additional attributes to the trace.
The @observe() decorator provides a convenient way to automatically wrap your instrumented code and add additional attributes to the trace.
from langfuse import observe, propagate_attributes, get_client
langfuse = get_client()
@observe()
def my_llm_pipeline(input):
# Add additional attributes (user_id, session_id, metadata, version, tags) to all spans created within this execution scope
with propagate_attributes(
user_id="user_123",
session_id="session_abc",
tags=["agent", "my-trace"],
metadata={"email": "user@langfuse.com"},
version="1.0.0"
):
# YOUR APPLICATION CODE HERE
result = call_llm(input)
# Update the trace input and output
langfuse.update_current_trace(
input=input,
output=result,
)
return resultLearn more about using the Decorator in the Langfuse SDK instrumentation docs.
Troubleshooting
No traces appearing
First, enable debug mode in the Python SDK:
export LANGFUSE_DEBUG="True"Then run your application and check the debug logs:
- OTel spans appear in the logs: Your application is instrumented correctly but traces are not reaching Langfuse. To resolve this:
- Call
langfuse.flush()at the end of your application to ensure all traces are exported. - Verify that you are using the correct API keys and base URL.
- Call
- No OTel spans in the logs: Your application is not instrumented correctly. Make sure the instrumentation runs before your application code.
Unwanted observations in Langfuse
The Langfuse SDK is based on OpenTelemetry. Other libraries in your application may emit OTel spans that are not relevant to you. These still count toward your billable units, so you should filter them out. See Unwanted spans in Langfuse for details.
Missing attributes
Some attributes may be stored in the metadata object of the observation rather than being mapped to the Langfuse data model. If a mapping or integration does not work as expected, please raise an issue on GitHub.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application:
Interoperability with the Python SDK
- Check the Novita AI Documentation for further details on available models and API options.
- Visit Langfuse to learn more about monitoring and tracing capabilities for your LLM applications.