Synthetic Dataset Generation for LLM Evaluation
In this notebook, we will explore how to generate synthetic datasets using language models and uploading them to Langfuse for evaluation.
What are Langfuse Datasets?
In Langfuse, a dataset is a collection of dataset items, each typically containing an input (e.g., user prompt/question), expected_output (the ground truth or ideal answer) and optional metadata.
Datasets are used for evaluation. You can run your LLM or application on each item in a dataset and compare the application’s responses to the expected outputs. This way, you can track performance over time and across different application configs (e.g. model versions or prompt changes).
Cases your Dataset Should Cover
Happy path – straightforward or common queries:
- “What is the capital of France?”
- “Convert 5 USD to EUR.”
Edge cases – unusual or complex:
- Very long prompts.
- Ambiguous queries.
- Very technical or niche.
Adversarial cases – malicious or tricky:
- Prompt injection attempts (“Ignore all instructions and …”).
- Content policy violations (harassment, hate speech).
- Logic traps (trick questions).
Examples
Example 1: Looping Over OpenAI API
We’ll use OpenAI’s API in a simple loop to create synthetic questions for an airline chatbot. You could similarly prompt the model to generate both questions and answers. %pip install openai langfuse
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Verify connection
if langfuse.auth_check():
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
else:
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!
from openai import OpenAI
import pandas as pd
client = OpenAI()
# Function to generate airline questions
def generate_airline_questions(num_questions=20):
questions = []
for i in range(num_questions):
completion = client.chat.completions.create(
model="gpt-4o",
messages=[
{
"role": "system",
"content": (
"You are a helpful customer service chatbot for an airline. "
"Please generate a short, realistic question from a customer."
)
}
],
temperature=1
)
question_text = completion.choices[0].message.content.strip()
questions.append(question_text)
return questions
# Generate 20 airline-related questions
airline_questions = generate_airline_questions(num_questions=20)
# Convert to a Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.DataFrame({"Question": airline_questions})from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Create a new dataset in Langfuse
dataset_name = "openai_synthetic_dataset"
langfuse.create_dataset(
name=dataset_name,
description="Synthetic Q&A dataset generated via OpenAI in a loop",
metadata={"approach": "openai_loop", "category": "mixed"}
)
# Upload each Q&A as a dataset item
for _, row in df.iterrows():
langfuse.create_dataset_item(
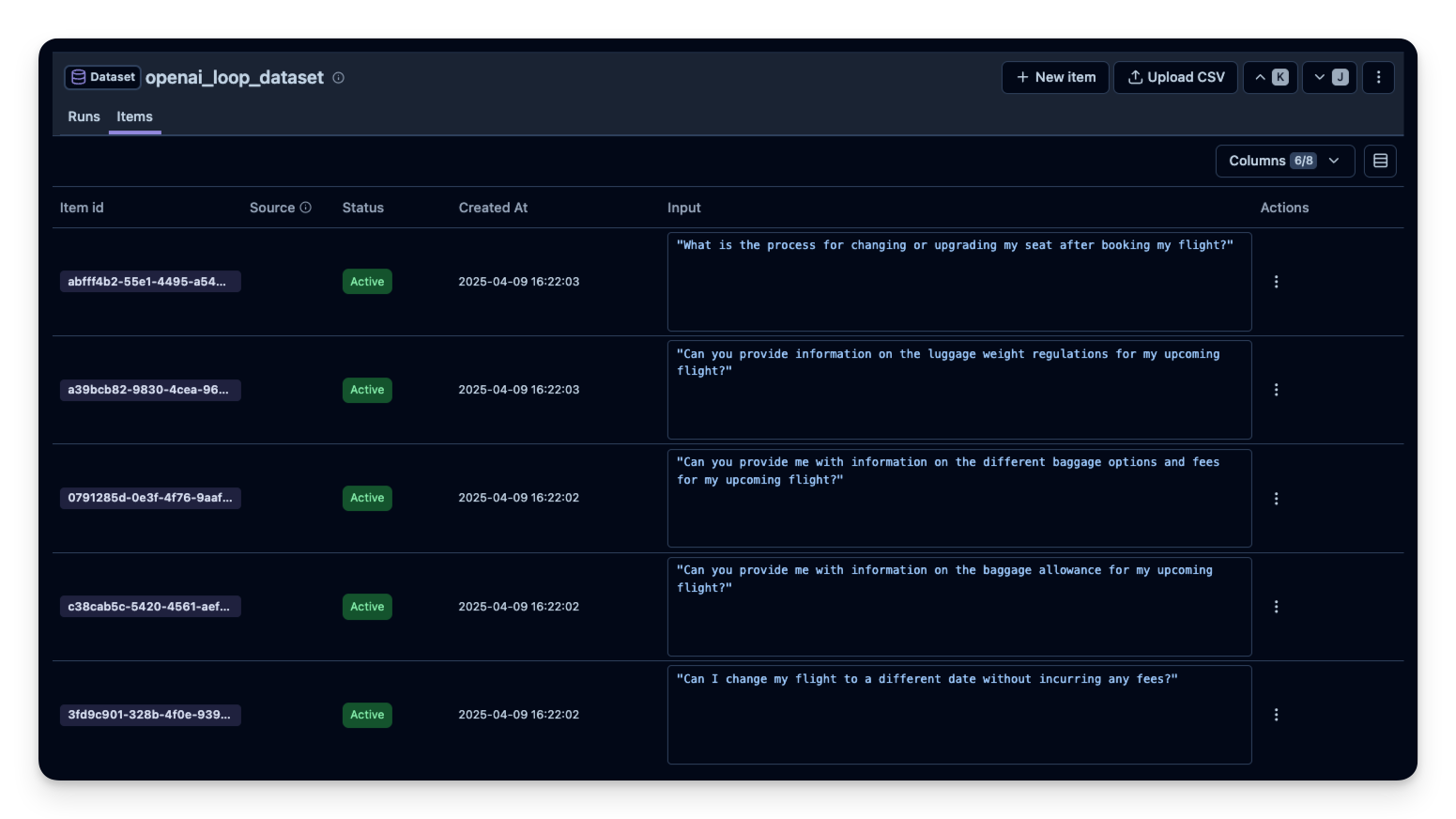
dataset_name="openai_loop_dataset",
input = row["Question"]
)
Example 2: RAGAS Library
For RAG, we often want questions that are grounded in specific documents. This ensures the question can be answered by the context, allowing us to evaluate how well a RAG pipeline retrieves and uses the context.
RAGAS is a library that can automate test set generation for RAG. It can take a corpus and produce relevant queries and answers. We’ll do a quick example:
Note: This example is taken from the RAGAS documentation
%pip install ragas langchain-community langchain-openai unstructured!git clone https://huggingface.co/datasets/explodinggradients/Sample_Docs_Markdownfrom langchain_community.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
path = "Sample_Docs_Markdown"
loader = DirectoryLoader(path, glob="**/*.md")
docs = loader.load()from ragas.llms import LangchainLLMWrapper
from ragas.embeddings import LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
generator_llm = LangchainLLMWrapper(ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o"))
generator_embeddings = LangchainEmbeddingsWrapper(OpenAIEmbeddings())from ragas.testset import TestsetGenerator
generator = TestsetGenerator(llm=generator_llm, embedding_model=generator_embeddings)
dataset = generator.generate_with_langchain_docs(docs, testset_size=10)
# 4. The result `testset` can be converted to a pandas DataFrame for inspection
df = dataset.to_pandas()from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# 5. Push the RAGAS-generated testset to Langfuse
langfuse.create_dataset(
name="ragas_generated_testset",
description="Synthetic RAG test set (RAGAS)",
metadata={"source": "RAGAS", "docs_used": len(docs)}
)
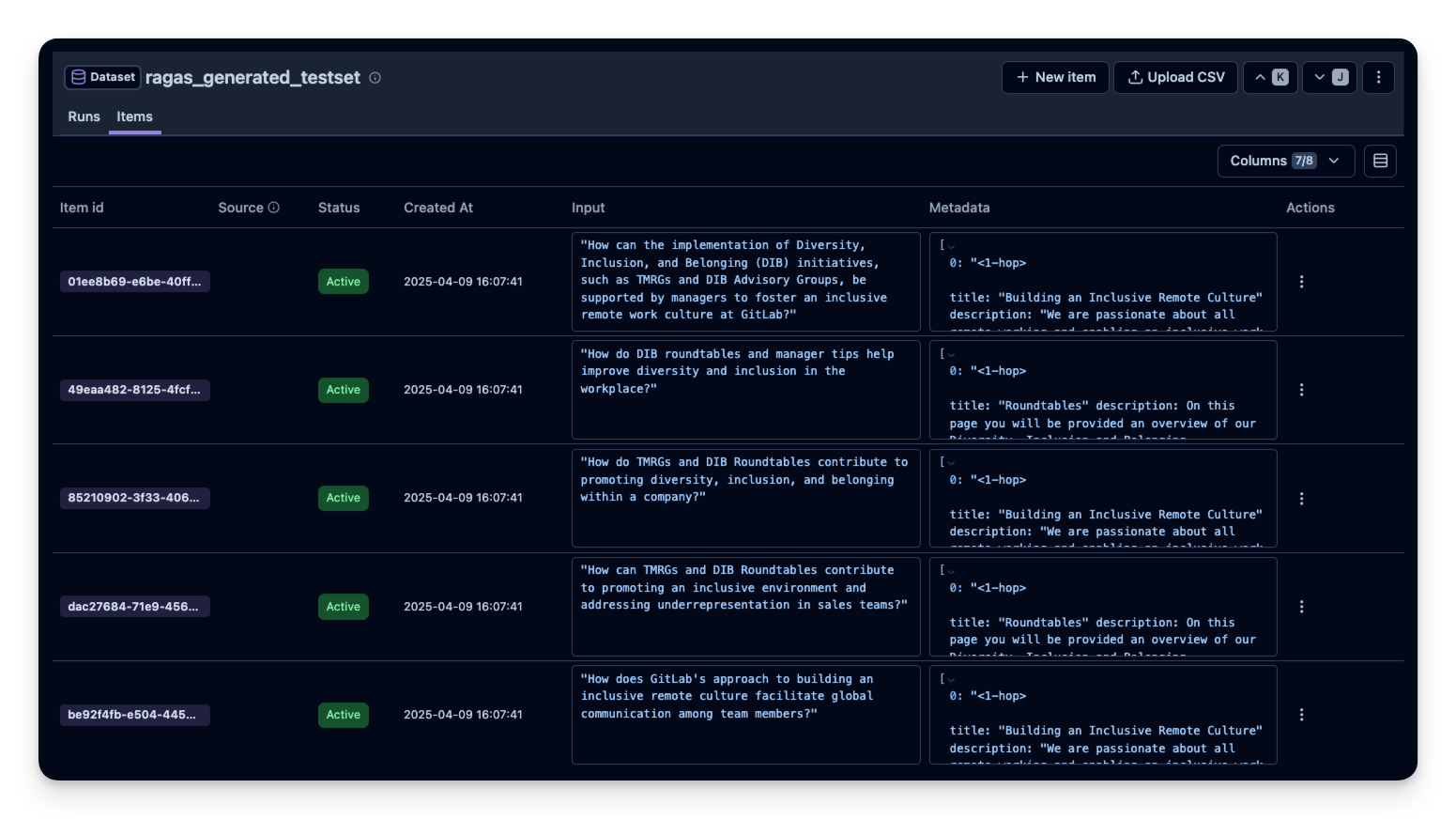
for _, row in df.iterrows():
langfuse.create_dataset_item(
dataset_name="ragas_generated_testset",
input = row["user_input"],
metadata = row["reference_contexts"]
)
Example 3: DeepEval Library
DeepEval is a library that helps generate synthetic data systematically using the Synthesizer class.
%pip install deepevalimport os
from langfuse import get_client
from deepeval.synthesizer import Synthesizer
from deepeval.synthesizer.config import StylingConfig# 1. Define the style we want for our synthetic data.
# For instance, we want user questions and correct SQL queries.
styling_config = StylingConfig(
input_format="Questions in English that asks for data in database.",
expected_output_format="SQL query based on the given input",
task="Answering text-to-SQL-related queries by querying a database and returning the results to users",
scenario="Non-technical users trying to query a database using plain English.",
)
# 2. Initialize the Synthesizer
synthesizer = Synthesizer(styling_config=styling_config)
# 3. Generate synthetic items from scratch, e.g. 20 items for a short demo
synthesizer.generate_goldens_from_scratch(num_goldens=20)
# 4. Access the generated examples
synthetic_goldens = synthesizer.synthetic_goldensfrom langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# 5. Create a Langfuse dataset
deepeval_dataset_name = "deepeval_synthetic_data"
langfuse.create_dataset(
name=deepeval_dataset_name,
description="Synthetic text-to-SQL data (DeepEval)",
metadata={"approach": "deepeval", "task": "text-to-sql"}
)
# 6. Upload the items
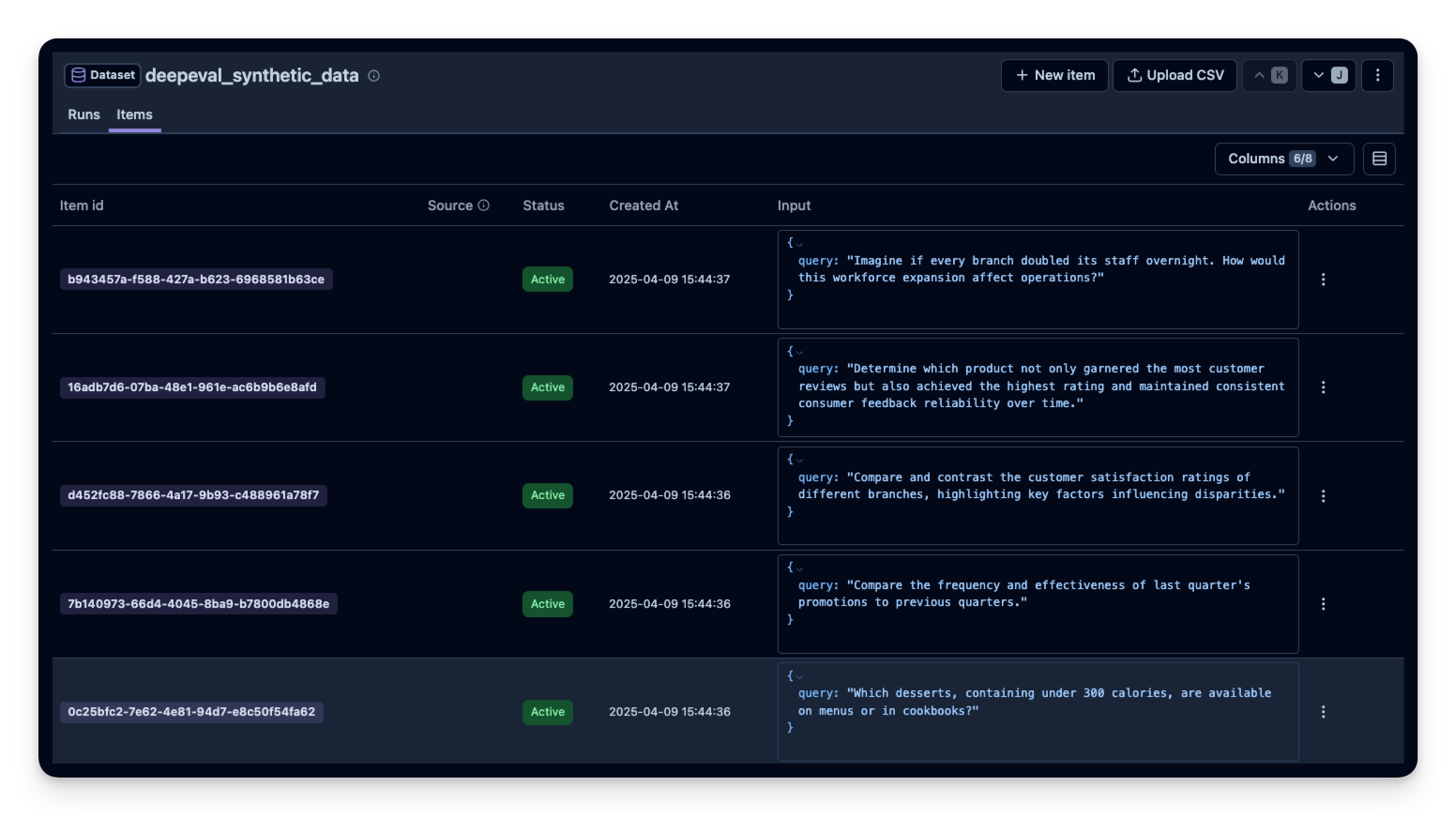
for golden in synthetic_goldens:
langfuse.create_dataset_item(
dataset_name=deepeval_dataset_name,
input={"query": golden.input},
)
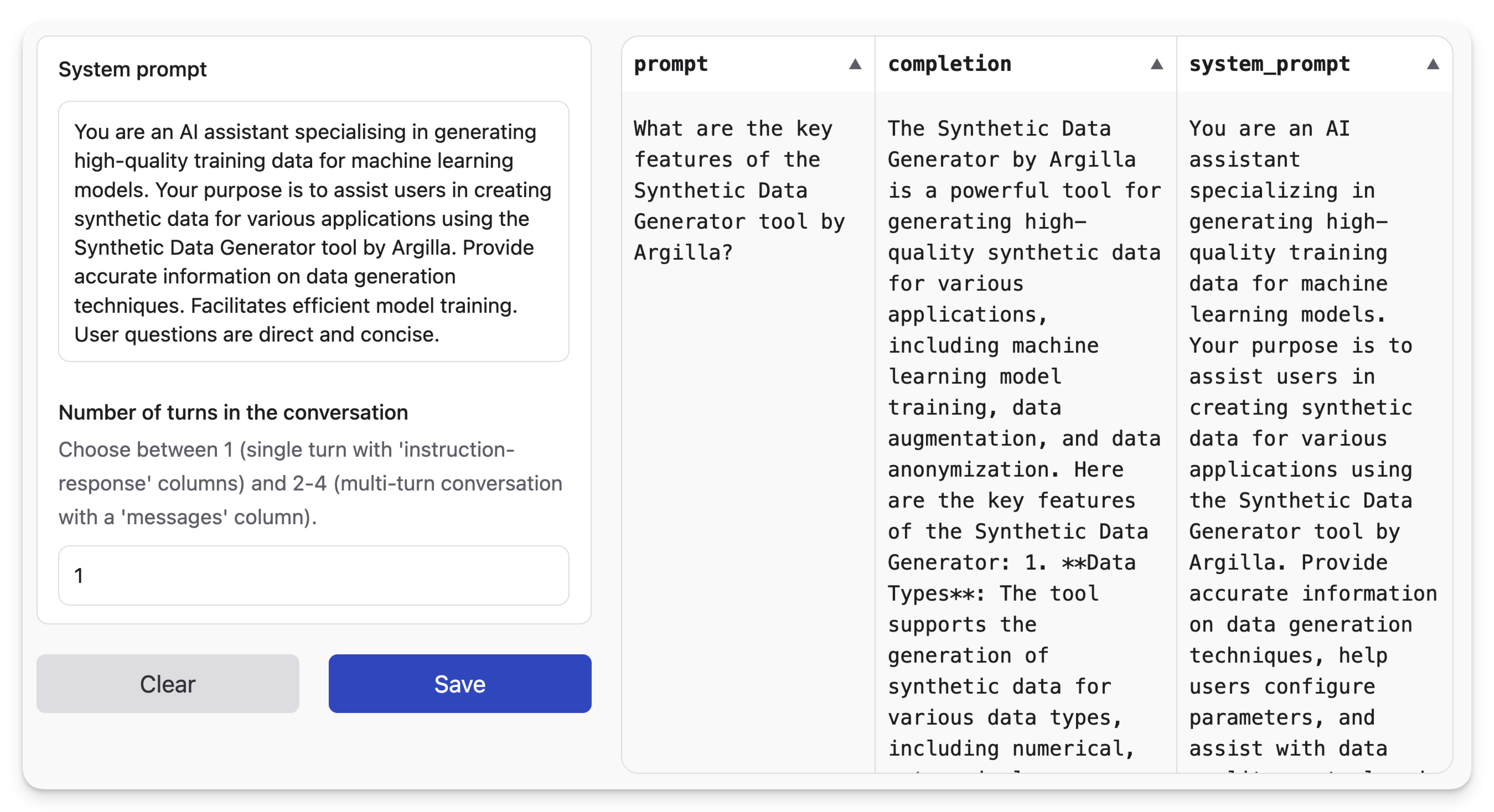
Example 4: No-Code via Hugging Face Dataset Generator
If you prefer a more UI-based approach, check out Hugging Face’s Synthetic Data Generator. You can generate examples in the Hugging Face UI. Then you can download them as CSV and upload it in the Langfuse UI.
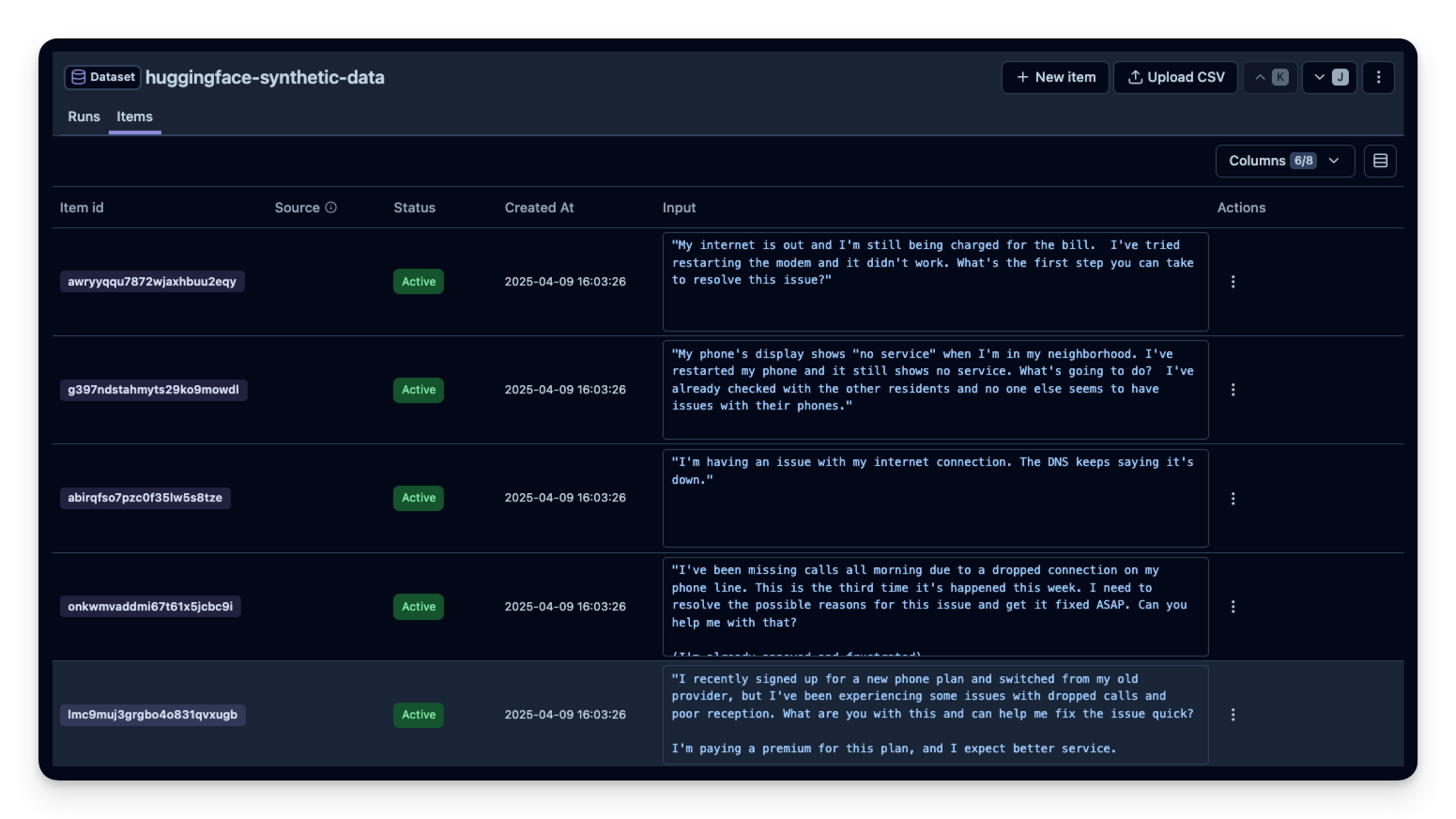
Example 5: RAG Dataset Generation
If you have an existing vector database or prefer not to use specialized libraries like RAGAS or DeepEval, you can generate a RAG testset by directly looping through your vector store. This approach gives you full control over the generation process.
This is useful when you:
- Want lightweight code without additional dependencies
- Need to customize the question generation logic
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."# Install dependencies
%pip install --upgrade langchain-community langchain-openai langchain-chroma langfuse "unstructured[md]"# Clone an example document set
!git clone https://huggingface.co/datasets/explodinggradients/Sample_Docs_Markdown# Load the documents
from langchain_community.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader
path = "Sample_Docs_Markdown"
loader = DirectoryLoader(path, glob="**/*.md")
docs = loader.load()from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI, OpenAIEmbeddings
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_text_splitters import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
# Chunk the documents
splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size=1000, chunk_overlap=200)
chunks = splitter.split_documents(docs)
# Create vector DB
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(chunks, OpenAIEmbeddings())# Generate questions
import json
# Get all chunks
all_chunks = vectorstore.get()['documents'][:10] # Get the first 10 chunks
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini")
test_items = []
for chunk in all_chunks:
# Ask LLM to generate one question
response = llm.invoke(
f"Generate one natural question that can be answered using this text. "
f"Return only JSON: {{\"question\": \"...\", \"answer\": \"...\"}}\n\n{chunk}"
)
# Parse response
content = response.content
if "```" in content:
content = content.split("```")[1].replace("json", "").strip()
qa = json.loads(content)
test_items.append({
"question": qa["question"],
"answer": qa["answer"],
"context": chunk
})# Push to Langfuse Dataset
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
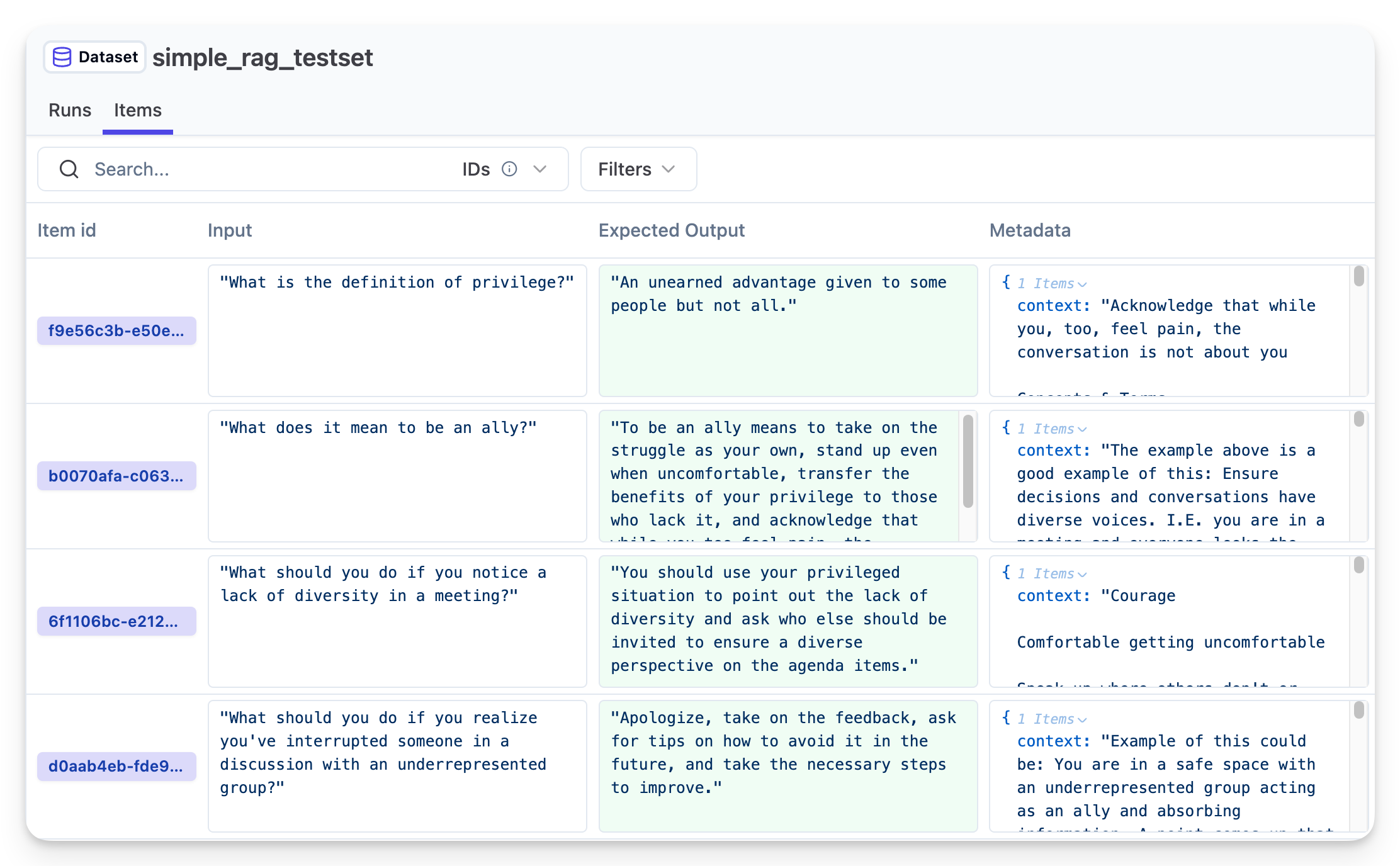
langfuse.create_dataset(name="simple_rag_testset")
for item in test_items:
langfuse.create_dataset_item(
dataset_name="simple_rag_testset",
input=item["question"],
expected_output=item["answer"],
metadata={"context": item["context"]}
)
print(f"✓ Created {len(test_items)} test items")You can now evaluate your application using this dataset. Check our RAG Observability and Evals blogpost to learn more.
Example 6: Torque - Declarative Dataset Generation
Torque is a declarative, typesafe DSL for building synthetic datasets. It lets you compose conversations like React components, making it particularly useful for generating complex multi-turn conversations with tool calls.
This approach is ideal when you need:
- Structured conversations with tool usage patterns
- Type-safe dataset generation with full TypeScript support
- Reproducible datasets with seeded generation
- Complex multi-turn dialogs that follow specific patterns
import { Langfuse } from "langfuse";
import {
oneOf,
generatedUser,
generatedAssistant,
generatedToolCall,
generatedToolCallResult,
times,
between,
generateDataset,
} from "@qforge/torque";
import { weatherTool, searchEmailTool } from "@qforge/torque/examples";
import { openai } from "@ai-sdk/openai";
const langfuse = new Langfuse({
publicKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY,
secretKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY,
baseUrl: process.env.LANGFUSE_URL,
});
// Generate dataset with Torque's declarative DSL
const conversationSchema = () => {
// Randomly select which tool to use in this conversation
const selectedTool = oneOf([searchEmailTool, weatherTool]);
return [
// Register the tool function
selectedTool.toolFunction(),
// User initiates request
generatedUser({
prompt: `User asking a question that will require calling ${selectedTool.name} tool.`,
}),
// Assistant acknowledges and calls tool
generatedAssistant({
prompt: "Assistant acknowledging the tool call",
toolCalls: [generatedToolCall(selectedTool, "tool-1")],
}),
generatedToolCallResult(selectedTool, "tool-1"),
// Assistant presents results
generatedAssistant({
prompt:
"Assistant responding to the user's question using the result of the tool call.",
}),
// Optional follow-up conversation (1-2 exchanges)
times(between(1, 2), [
generatedUser({
prompt: "Follow-up question",
}),
generatedAssistant({
prompt:
"Assistant responding to the user's follow-up question",
}),
]),
];
};
// Generate the dataset to a JSONL file
await generateDataset(conversationSchema, {
count: 50,
model: openai("gpt-5-mini"),
output: "data/torque_tool.jsonl",
seed: 42, // Reproducible generation
});
// Read generated JSONL and upload to Langfuse
await langfuse.createDataset({
name: "torque_tool",
description: "Tool calling conversations generated with Torque DSL",
});
const jsonlContent = await Bun.file("data/torque_tool.jsonl").text();
const conversations = jsonlContent
.trim()
.split("\n")
.map((line) => JSON.parse(line));
for (const conversation of conversations) {
await langfuse.createDatasetItem({
datasetName: "torque_tool",
input: conversation.messages,
metadata: {
tool_used: conversation.messages.find((m) => m.role === "tool")?.name,
turns: conversation.messages.length,
},
});
}
await langfuse.flushAsync();
Key advantages of Torque:
- Type-safe conversations: Full TypeScript support with Zod schemas ensures your synthetic data matches your production types
- Declarative patterns: Compose complex conversation flows with
times(),oneOf(), and other combinators - Tool simulation: Built-in support for tool calls and results, perfect for evaluating agentic applications
- Reproducible: Seeded generation ensures identical datasets across runs
- Realistic variations: AI generates natural variations while following your structural constraints
This approach is particularly powerful for evaluating AI agents with tool usage, as it generates structurally consistent but semantically diverse conversations.
Next Steps
- Explore your dataset in Langfuse. You can see each dataset in the UI.
- Run experiments You can now evaluate your application using this dataset.
- Compare runs over time or across models, prompts, or chain logic.
For more details on how to run experiments on a dataset, see the Langfuse docs.