Cookbook: Langfuse JS/TS SDK
JS/TS applications can either be traced via the Langfuse JS/TS SDK, or by using one of the native integrations such as OpenAI, LangChain or Vercel AI SDK.
In this notebook, we will walk you through a simple end-to-end example that:
- Shows how to log any LLM call via the low-level SDK methods
- Uses integrations that are interoperable with low-level SDK
- LangChain integration
- OpenAI integration
- Vercel AI SDK
For this guide, we assume that you are already familiar with the Langfuse data model (traces, spans, generations, etc.). If not, please read the conceptual introduction to tracing.
Set Up Environment
Get your Langfuse API keys by signing up for Langfuse Cloud or self-hosting Langfuse. You’ll also need your OpenAI API key.
Note: This cookbook uses Deno.js for execution, which requires different syntax for importing packages and setting environment variables. For Node.js applications, the setup process is similar but uses standard
npmpackages andprocess.env.
// Langfuse authentication keys
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY", "pk-lf-***");
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY", "sk-lf-***");
// Langfuse host configuration
// For US data region, set this to "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com"
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_BASE_URL", "https://cloud.langfuse.com")
// Set environment variables using Deno-specific syntax
Deno.env.set("OPENAI_API_KEY", "sk-proj-***");With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the langfuseSpanProcessor which is passed to the main OpenTelemetry SDK that orchestrates tracing.
// Import required dependencies
import 'npm:dotenv/config';
import { NodeSDK } from "npm:@opentelemetry/sdk-node";
import { LangfuseSpanProcessor } from "npm:@langfuse/otel";
// Export the processor to be able to flush it later
// This is important for ensuring all spans are sent to Langfuse
export const langfuseSpanProcessor = new LangfuseSpanProcessor({
publicKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY!,
secretKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY!,
baseUrl: process.env.LANGFUSE_BASE_URL ?? 'https://cloud.langfuse.com', // Default to cloud if not specified
environment: process.env.NODE_ENV ?? 'development', // Default to development if not specified
});
// Initialize the OpenTelemetry SDK with our Langfuse processor
const sdk = new NodeSDK({
spanProcessors: [langfuseSpanProcessor],
});
// Start the SDK to begin collecting telemetry
// The warning about crypto module is expected in Deno and doesn't affect basic tracing functionality. Media upload features will be disabled, but all core tracing works normally
sdk.start();The LangfuseClient provides additional functionality beyond OpenTelemetry tracing, such as scoring, prompt management, and data retrieval. It automatically uses the same environment variables we set earlier.
import { LangfuseClient } from "npm:@langfuse/client";
const langfuse = new LangfuseClient();Log LLM Calls
You can use the SDK to log any LLM call or any of the integrations that are interoperable with it.
In the following, we will demonstrate how to log LLM calls using the SDK, LangChain, Vercel AI SDK, and OpenAI integrations.
Option 1: Context Manager
To simplify nesting and context management, you can use startActiveObservation. These functions take a callback and automatically manage the observation’s lifecycle and the OpenTelemetry context. Any observation created inside the callback will automatically be nested under the active observation, and the observation will be ended when the callback finishes.
This is the recommended approach for most use cases as it prevents context leakage and ensures observations are properly ended.
// Import necessary functions from the tracing package
import { startActiveObservation, startObservation, updateActiveTrace, updateActiveObservation } from "npm:@langfuse/tracing";
// Start a new span with automatic context management
await startActiveObservation("context-manager", async (span) => {
// Log the initial user query
span.update({
input: { query: "What is the capital of France?" }
});
// Create a new generation span that will automatically be a child of "context-manager"
const generation = startObservation(
"llm-call",
{
model: "gpt-4",
input: [{ role: "user", content: "What is the capital of France?" }],
},
{ asType: "generation" },
);
// ... LLM call logic would go here ...
// Update the generation with token usage statistics
generation.update({
usageDetails: {
input: 10, // Number of input tokens
output: 5, // Number of output tokens
cache_read_input_tokens: 2, // Tokens read from cache
some_other_token_count: 10, // Custom token metric
total: 17, // Optional: automatically calculated if not provided
},
});
// End the generation with the LLM response
generation.update({
output: { content: "The capital of France is Paris." },
}).end();
// Example user information
const user = { id: "user-5678", name: "Jane Doe", sessionId: "123" };
// Add an optional log level of type warning to the active span
updateActiveObservation(
{ level: "WARNING", statusMessage: "This is a warning" },
);
// Update the trace with user context
updateActiveTrace({
userId: user.id,
sessionId: user.sessionId,
metadata: { userName: user.name },
});
// Mark the span as complete with final output
span.update({ output: "Successfully answered." });
});
// Ensure all spans are sent to Langfuse
await langfuseSpanProcessor.forceFlush();Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Option 2: observe Decorator
The observe wrapper is a powerful tool for tracing existing functions without modifying their internal logic. It acts as a decorator that automatically creates a span or generation around the function call. You can use the updateActiveObservation function to add attributes to the observation from within the wrapped function.
import { observe, updateActiveObservation } from "npm:@langfuse/tracing";
// An existing function
async function fetchData(source: string) {
updateActiveObservation({ usageDetails: {
// usage
input: 10,
output: 5,
}, { asType: 'generation' }
})
// ... logic to fetch data
return { data: `some data from ${source}` };
}
// Wrap the function to trace it
const tracedFetchData = observe(fetchData, {
name: "observe-wrapper",
asType: "generation",
});
// Now, every time you call tracedFetchData, a span is created.
// Its input and output are automatically populated with the
// function's arguments and return value.
const result = await tracedFetchData("API");
await langfuseSpanProcessor.forceFlush();Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Option 3: Manual Spans
This part shows how to log any LLM call by passing the model in and outputs via the Langfuse SDK.
Steps:
- Create span to contain this section within the trace
- Create generation, log input and model name as it is already known
- Call the LLM SDK and log the output
- End generation and span
Teams typically wrap their LLM SDK calls in a helper function that manages tracing internally. This implementation occurs once and is then reused for all LLM calls.
// Import the startObservation function for manual span creation
import { startObservation } from 'npm:@langfuse/tracing';
// Create the root span for this operation
const span = startObservation('manual-observation', {
input: { query: 'What is the capital of France?' },
});
// Create a child span for a tool call (e.g., weather API)
const toolCall = span.startObservation(
'fetch-weather',
{ input: { city: 'Paris' } },
{ asType: "tool" },
);
// Simulate API call with timeout
await new Promise((r) => setTimeout(r, 100));
// End the tool call with its output
toolCall.update({ output: { temperature: '15°C' } }).end();
// Create a generation span for the LLM call
const generation = span.startObservation(
'llm-call',
{
model: 'gpt-4',
input: [{ role: 'user', content: 'What is the capital of France?' }],
output: { content: 'The capital of France is Paris.' },
},
{ asType: "generation" },
);
// Update the generation with token usage details
generation.update({
usageDetails: {
input: 10, // Input token count
output: 5, // Output token count
cache_read_input_tokens: 2, // Cached tokens used
some_other_token_count: 10, // Custom metric
total: 17, // Total tokens (optional)
},
});
// End the generation with final output
generation.update({
output: { content: 'The capital of France is Paris.' },
}).end();
// End the root span with final status and session ID
span.update({
output: 'Successfully answered user request.',
sessionId: '123'
}).end();
// Ensure all spans are flushed to Langfuse
await langfuseSpanProcessor.forceFlush();Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Native integrations
Besides manual creation of spans using the SDK methods (decorator, context manager and manual creation), you can also use the native instrumentations for OpenAI or Langchain to automatically capture all generation details.
Option 1: Using OpenAI
This step shows how to trace OpenAI applications using the OpenAI integration which is interoperable with the Langfuse SDK.
Since this is a native integration, the model parameters and outputs are automatically captured.
// Import required packages
import OpenAI from "npm:openai@^4";
import { observeOpenAI } from "npm:@langfuse/openai";
// Initialize the OpenAI client
const openai = new OpenAI();
// Wrap the OpenAI client with Langfuse tracing
const tracedOpenAI = observeOpenAI(openai, {
// Configure trace-level attributes for all API calls
traceName: "my-openai-trace", // Name for the trace
sessionId: "user-session-123", // Track user session
userId: "user-abc", // Track user identity
tags: ["openai-integration"], // Add searchable tags
});
// Make an API call using the traced client
// All parameters and responses will be automatically captured
const completion = await tracedOpenAI.chat.completions.create({
model: "gpt-4",
messages: [{ role: "user", content: "What is OpenTelemetry?" }],
});Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Option 2: Using LangChain
This step shows how to trace LangChain applications using the LangChain integration which is fully interoperable with the Langfuse SDK.
Since this is a native integration, the model parameters and outputs are automatically captured.
// Import required LangChain and Langfuse packages
import { ChatOpenAI } from "npm:@langchain/openai";
import { ChatPromptTemplate } from "npm:@langchain/core/prompts";
import { CallbackHandler } from "npm:@langfuse/langchain";
// Initialize the Langfuse callback handler with tracing configuration
const langfuseHandler = new CallbackHandler({
sessionId: "user-session-123", // Track user session
userId: "user-abc", // Track user identity
tags: ["langchain-test"], // Add searchable tags
});
// Define the LangChain components
const model = new ChatOpenAI({ model: "gpt-4o" }); // Initialize LLM
const prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.fromTemplate("Tell me a joke about {topic}."); // Create prompt template
const chain = prompt.pipe(model); // Combine prompt and model into a chain
// Execute the chain with Langfuse tracing
const result = await chain.invoke(
{ topic: "developers" }, // Input variables for the prompt
{
callbacks: [langfuseHandler], // Enable Langfuse tracing
runName: "joke-generator", // Name for the trace (if no active span)
}
);
// Output the result
console.log(result.content);Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Option 3: Vercel AI SDK
The Vercel AI SDK offers native instrumentation with OpenTelemetry. To send spans to your Langfuse instance, you need to set experimental_telemetry: {isEnabled: true}.
// Import Vercel AI SDK components
import { generateText } from "npm:ai"
import { openai } from "npm:@ai-sdk/openai"
// Generate text with OpenTelemetry tracing enabled
const result_3 = await generateText({
model: openai('gpt-4.1'), // Specify the OpenAI model
prompt: 'Write a short story about a cat.', // The prompt for generation
experimental_telemetry: {
isEnabled: true, // Enable OpenTelemetry tracing
functionId: 'my-awesome-function', // Identify the function being traced
metadata: {
something: 'custom', // Custom metadata fields
someOtherThing: 'other-value',
sessionId: '123', // Track user session
userId: '456', // Track user identity
tags: ['test', 'langfuse'], // Add searchable tags
},
},
});[Public trace in the Langfuse UI](Public trace in the Langfuse UI)
Step 5: View the Traces in Langfuse
After ingesting your spans, you can view them in your Langfuse dashboard.
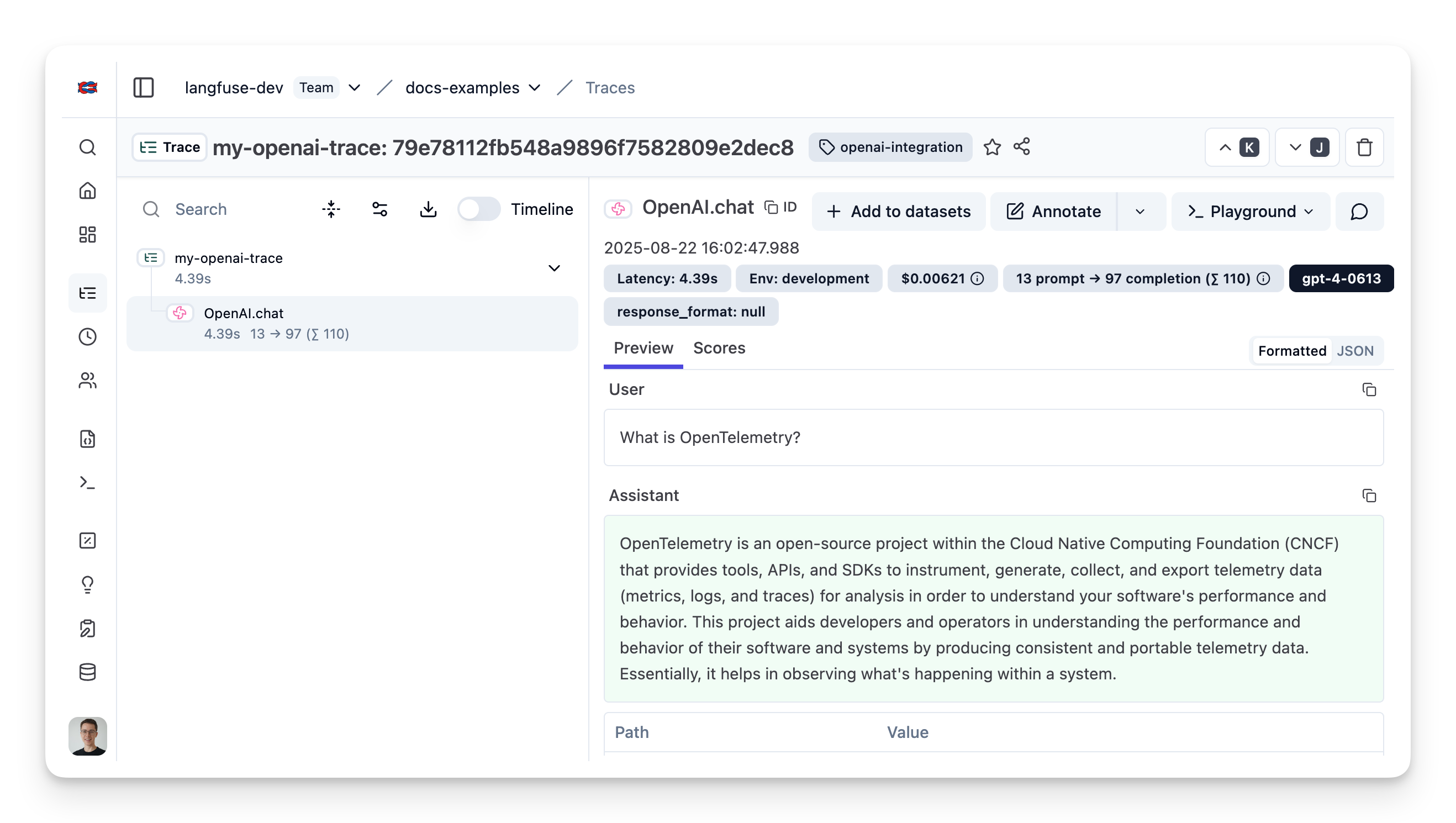
Example trace in the Langfuse UI.