Example: Using OpenTelemetry SDK with Langfuse OTel API
This notebook demonstrates how to use any OpenTelemetry SDK to send traces to Langfuse. OpenTelemetry is a CNCF project that provides a standard way to collect distributed traces and metrics from applications.
Langfuse operates as an OpenTelemetry Backend and maps the received traces to the Langfuse data model according to the OpenTelemetry Gen AI Conventions. See the property mapping documentation for details on how attributes are parsed.
In this example, we’ll use the Python OpenTelemetry SDK to send traces with GenAI attributes to Langfuse.
Setup
⚠️ Note: We have a new OpenTelemetry native Langfuse SDK. Please check out the SDK v3 for a more powerful and simpler to use SDK.
%pip install opentelemetry-sdk opentelemetry-exporter-otlp opentelemetry-apiimport os
import base64
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
LANGFUSE_AUTH = base64.b64encode(
f"{os.environ.get('LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY')}:{os.environ.get('LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY')}".encode()
).decode()
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = os.environ.get("LANGFUSE_BASE_URL") + "/api/public/otel"
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"Configure tracer_provider and add a span processor to export traces to Langfuse. OTLPSpanExporter() uses the endpoint and headers from the environment variables.
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace import TracerProvider
from opentelemetry.exporter.otlp.proto.http.trace_exporter import OTLPSpanExporter
from opentelemetry.sdk.trace.export import SimpleSpanProcessor
trace_provider = TracerProvider()
trace_provider.add_span_processor(SimpleSpanProcessor(OTLPSpanExporter()))
# Sets the global default tracer provider
from opentelemetry import trace
trace.set_tracer_provider(trace_provider)
# Creates a tracer from the global tracer provider
tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)Flattened attributes
Opentelemetry lets you attach a set of attributes to all spans by setting set_attribute.
GenAI Semantic Convention Attributes:
with tracer.start_as_current_span("GenAI Attributes") as span:
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.prompt.0.role", "system")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.prompt.0.content", "You are a coding assistant that helps write Python code.")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.prompt.1.role", "user")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.prompt.1.content", "Write a function that calculates the factorial of a number.")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.completion.0.role", "assistant")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.completion.0.content", """def factorial(n):
if n == 0:
return 1
return n * factorial(n-1)""")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.request.model", "gpt-4")
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.request.temperature", 0.7)
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.usage.prompt_tokens", 25)
span.set_attribute("gen_ai.usage.completion_tokens", 45)Langfuse Attributes:
set_attribute allows you to set properties like a Langfuse Session ID, to group traces into Langfuse Sessions or a User ID, to assign traces to a specific user. You can find a list of all supported attributes in the here.
with tracer.start_as_current_span("Langfuse Attributes") as span:
span.set_attribute("langfuse.user.id", "user-123")
span.set_attribute("langfuse.session.id", "123456789")
span.set_attribute("langfuse.tags", ["staging", "demo"])
span.set_attribute("langfuse.prompt.name", "test-1")JSON-serialized attributes
Export a span using JSON-serialized attributes
with tracer.start_as_current_span("GenAI JSON-Serialized Attributes") as span:
span.set_attribute(
"gen_ai.prompt_json",
json.dumps(
[
{"role": "system", "content": "You are an expert art historian and critic."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Describe Vincent van Gogh's 'The Starry Night' painting in detail."},
]
),
)
span.set_attribute(
"gen_ai.completion_json",
json.dumps(
[
{"role": "assistant", "content": "The Starry Night (1889) is one of Van Gogh's most famous works, painted during his stay at the Saint-Paul-de-Mausole asylum. The painting depicts a night scene with a swirling sky filled with stars and a crescent moon over a village. The sky is dominated by luminous yellow stars and a spiral pattern of blue clouds. In the foreground, a dark cypress tree reaches toward the sky like a flame. The village below is quiet and peaceful, with a prominent church spire piercing the night. The brushwork is bold and expressive, with thick impasto strokes creating a sense of movement and energy throughout the composition."},
]
),
)Dataset Experiments when using OpenTelemetry
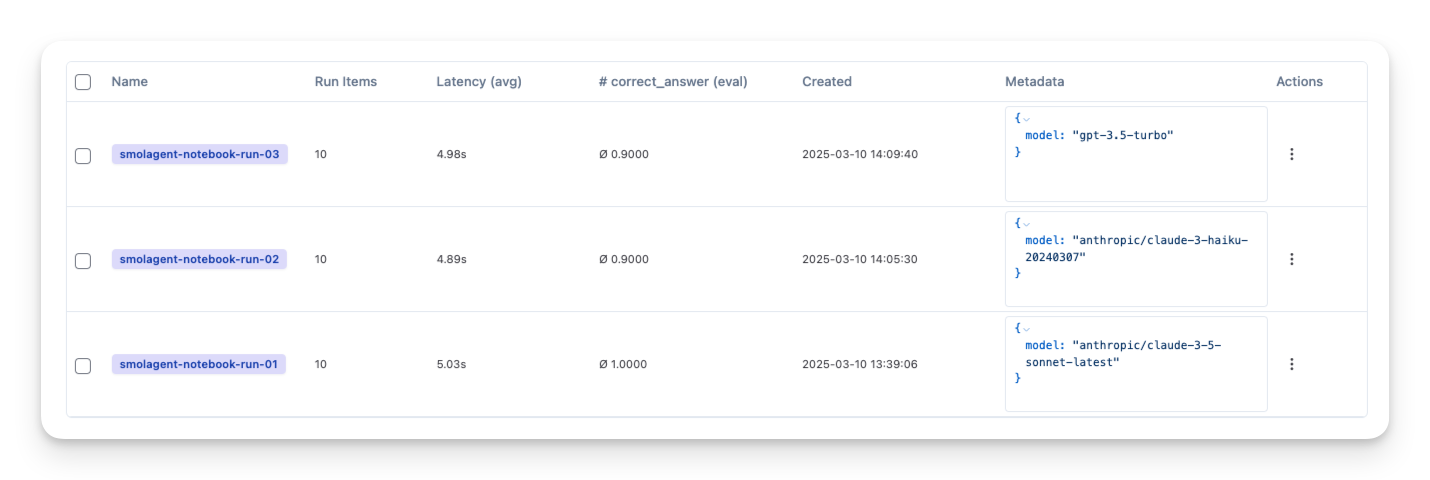
You can also test your smolagents using Langfuse Dataset Experiments:
- Create a benchmark dataset (with prompt and expected output pairs)
- Run your agent on that dataset
- Compare outputs to the expected results or use an additional scoring mechanism
Below, we demonstrate this approach with the GSM8K dataset, which contains math questions and solutions.
from opentelemetry.trace import format_trace_id
def otel_helper_function(input):
with tracer.start_as_current_observation("Otel-Trace") as span:
# Your gen ai application logic here: (make sure this function is sending traces to Langfuse)
output = your_application(input)
# Fetch the current span and trace id
current_span = trace.get_current_span()
span_context = current_span.get_span_context()
trace_id = span_context.trace_id
formatted_trace_id = format_trace_id(trace_id)
langfuse_trace = langfuse.trace(
id=formatted_trace_id,
input=input,
output=output
)
return langfuse_trace, outputThen loop over the dataset items and run the application.
from langfuse import Langfuse
langfuse = Langfuse()
dataset = langfuse.get_dataset("<langfuse_dataset_name>")
# Run our application against each dataset item
for item in dataset.items:
langfuse_trace, output = otel_helper_function(item.input["text"])
# Link the trace to the dataset item for analysis
item.link(
langfuse_trace,
run_name="run-01",
run_metadata={ "model": model.model_id }
)
# Optionally, store a quick evaluation score for demonstration
langfuse_trace.score(
name="<example_eval>",
value= your_evaluation_function(output),
comment="This is a comment"
)
# Flush data to ensure all telemetry is sent
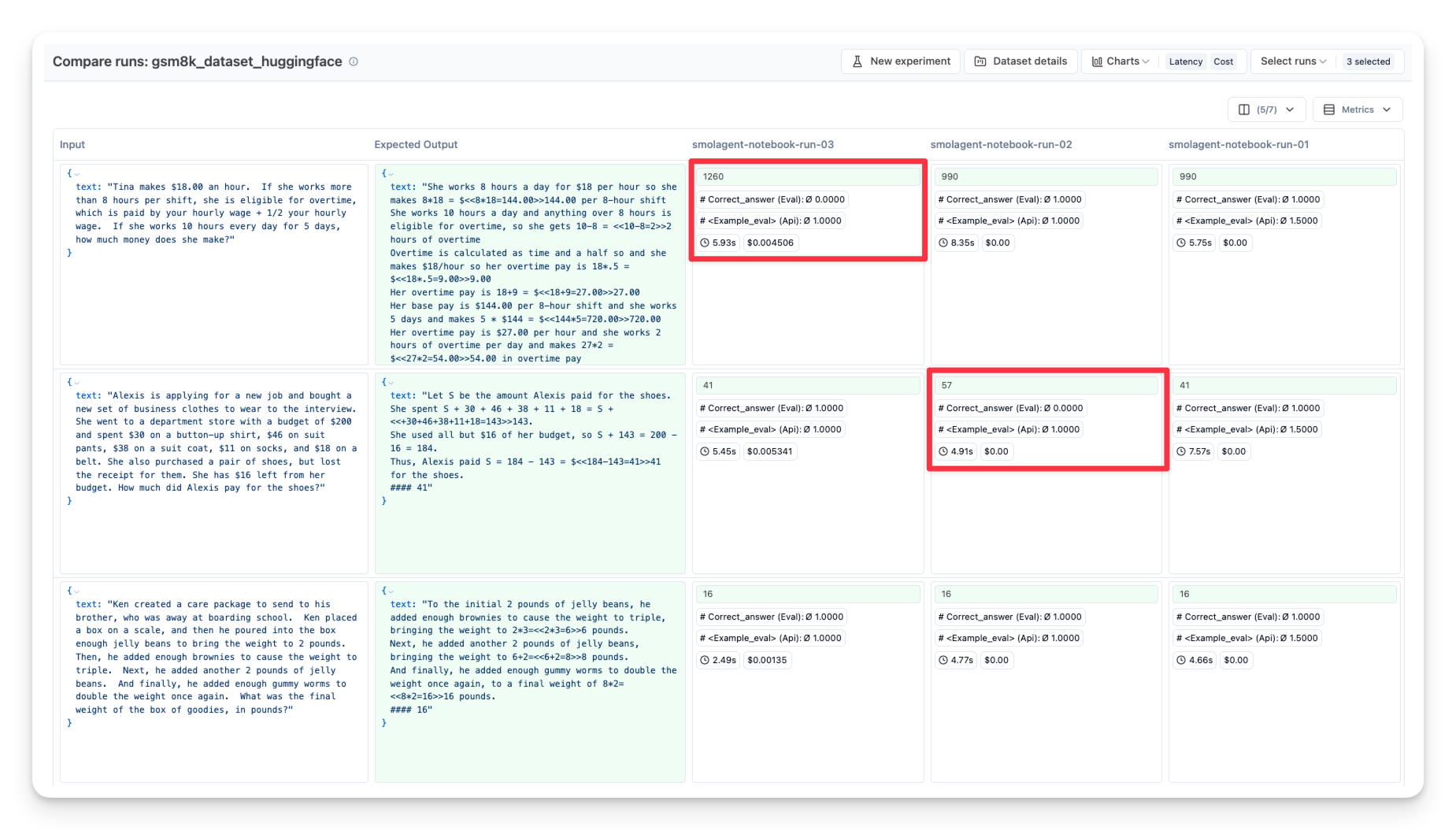
langfuse.flush()You can repeat this process with different:
- Models (OpenAI GPT, local LLM, etc.)
- Prompts (different system messages)
Then compare them side-by-side in your observability tool: