OpenLLMetry Integration via OpenTelemetry
Langfuse provides a backend built on OpenTelemetry for ingesting trace data, and you can use different instrumentation libraries to export traces from your applications. In this guide, we showcase how to instrument your LLM application using the OpenLLMetry instrumentation library by Traceloop.
About OpenLLMetry: OpenLLMetry is an open source project that simplifies monitoring and debugging of your LLM application. It leverages OpenTelemetry to collect trace data in a non-intrusive manner.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Begin by installing the necessary Python packages. In this example, we need the openai library to interact with OpenAI’s API and traceloop-sdk for enabling OpenLLMetry instrumentation.
%pip install openai traceloop-sdk langfuseStep 2: Configure Environment Variables
Before sending any requests, configure your environment with the necessary credentials and endpoints. Here, we set up Langfuse authentication by combining your public and secret keys into a Base64-encoded token. We also specify the Langfuse endpoint based on your desired geographical region (EU or US) and provide your OpenAI API key.
import os
import base64
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_BASE_URL"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Build Basic Auth header.
LANGFUSE_AUTH = base64.b64encode(
f"{os.environ.get('LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY')}:{os.environ.get('LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY')}".encode()
).decode()
# Configure OpenTelemetry endpoint & headers
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"] = os.environ.get("LANGFUSE_BASE_URL") + "/api/public/otel"
os.environ["OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_HEADERS"] = f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"
# Your openai key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Verify connection
if langfuse.auth_check():
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
else:
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!Step 3: Initialize Instrumentation
Next, initialize the OpenLLMetry instrumentation using the traceloop-sdk. Using disable_batch=True is recommended if you run this code in a notebook as traces are sent immediately without waiting for batching.
from traceloop.sdk import Traceloop
Traceloop.init(disable_batch=True,
api_endpoint=os.environ.get("OTEL_EXPORTER_OTLP_ENDPOINT"),
headers=os.environ.get(f"Authorization=Basic {LANGFUSE_AUTH}"),)[39m
ERROR:root:Error initializing redis instrumentor: No module named 'opentelemetry.instrumentation.redis'Step 4: Execute a Sample LLM Request
With instrumentation enabled, every OpenAI API call will now be traced. The following example sends a chat completion request to illustrate the integration.
from openai import OpenAI
openai_client = OpenAI()
chat_completion = openai_client.chat.completions.create(
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": "What is LLM Observability?",
}
],
model="gpt-4o-mini",
)
print(chat_completion)ChatCompletion(id='chatcmpl-BjRWj0Gn9A1PdPYslJ9rDNW730I97', choices=[Choice(finish_reason='stop', index=0, logprobs=None, message=ChatCompletionMessage(content="LLM observability refers to the practices, tools, and methodologies used to monitor, analyze, and understand the behavior and performance of Large Language Models (LLMs) in real time. As organizations increasingly rely on LLMs for various applications—such as natural language processing, chatbots, content generation, and more—ensuring their reliability, accuracy, and ethical alignment has become critical.\n\nKey components of LLM observability include:\n\n1. **Monitoring Performance**: Tracking metrics such as response time, resource utilization, and throughput to ensure that the model operates efficiently under load.\n\n2. **Quality Analysis**: Evaluating the quality of the model's outputs through various means, including user feedback, automated evaluation metrics, and comparison to ground truth data.\n\n3. **Behavior Analysis**: Analyzing the model's behavior in different contexts to identify biases, unintentional outputs, or other anomalies. This includes examining edge cases where the model might fail or produce unexpected results.\n\n4. **Debugging Tools**: Implementing tools that help trace issues or problems back to specific inputs, configurations, or model parameters that may be causing suboptimal performance.\n\n5. **Data Drift Detection**: Monitoring the input data for changes over time that could affect the model's performance, such as shifts in language use, terminology, or user behavior.\n\n6. **Feedback Loops**: Establishing mechanisms for continuous feedback from users and incorporating that information back into the model development lifecycle for fine-tuning and improvements.\n\n7. **Compliance and Safety**: Ensuring that the model adheres to ethical standards and legal requirements, especially regarding data usage and content generation.\n\nEffective observability can help organizations better manage their LLM deployments, minimize risks, and enhance the overall user experience by ensuring that models perform accurately and reliably in a wide range of scenarios.", refusal=None, role='assistant', annotations=[], audio=None, function_call=None, tool_calls=None))], created=1750170273, model='gpt-4o-mini-2024-07-18', object='chat.completion', service_tier='default', system_fingerprint='fp_34a54ae93c', usage=CompletionUsage(completion_tokens=368, prompt_tokens=14, total_tokens=382, completion_tokens_details=CompletionTokensDetails(accepted_prediction_tokens=0, audio_tokens=0, reasoning_tokens=0, rejected_prediction_tokens=0), prompt_tokens_details=PromptTokensDetails(audio_tokens=0, cached_tokens=0)))Step 5: View the Trace in Langfuse
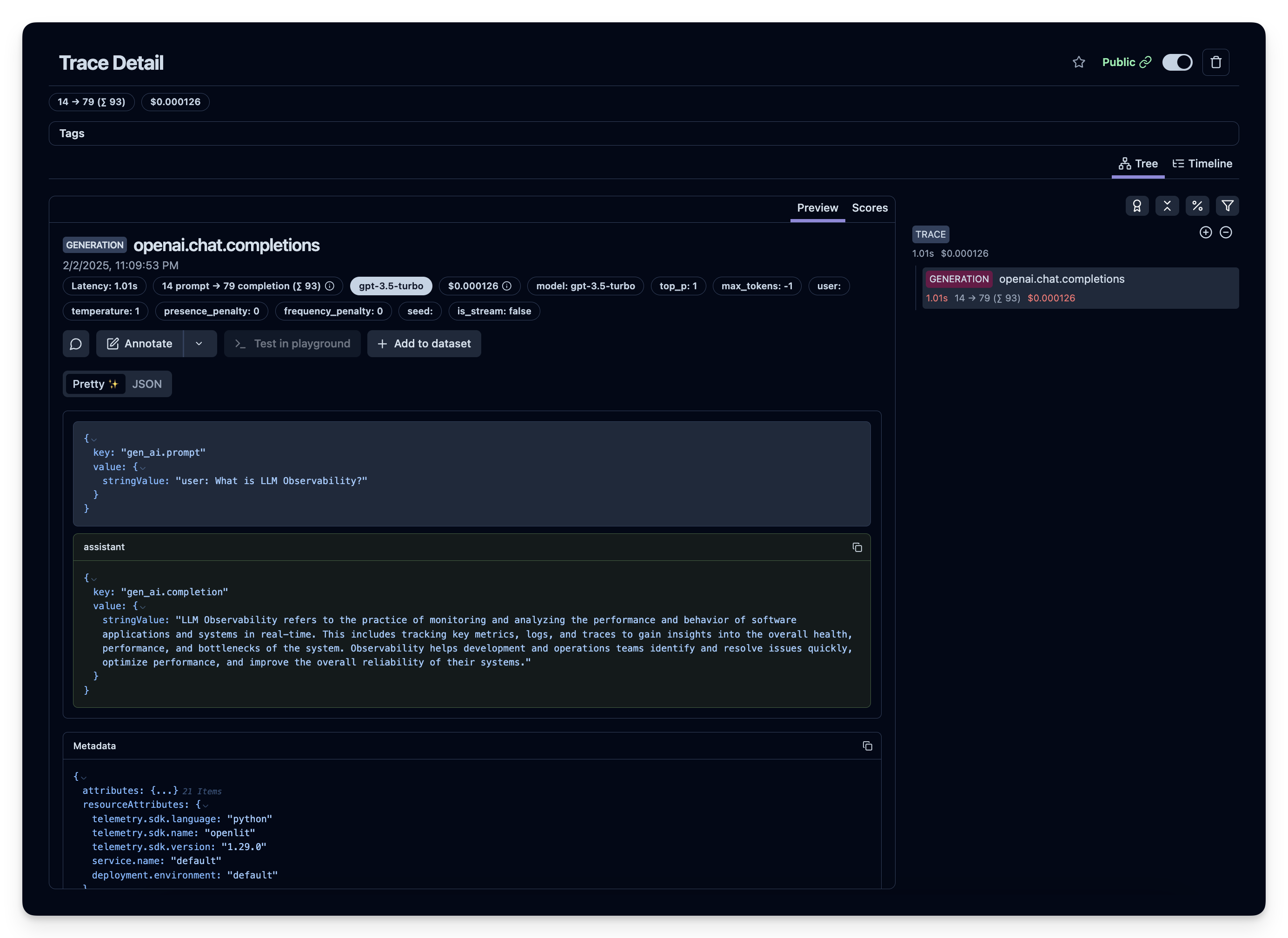
After running the above code, you can review the generated trace in your Langfuse dashboard: