Integrate Langfuse with Semantic Kernel
This notebook provides a step-by-step guide on integrating Langfuse with Semantic Kernel to achieve observability and debugging for your LLM applications. By following this tutorial, you will learn how to trace your Semantic Kernel applications using Langfuse, manage your prompts in one place and evaluate your application to make it production ready.
What is Semantic Kernel? Semantic Kernel (GitHub) is a powerful open-source SDK from Microsoft. It facilitates the combination of LLMs with popular programming languages like C#, Python, and Java. Semantic Kernel empowers developers to build sophisticated AI applications by seamlessly integrating AI services, data sources, and custom logic, accelerating the delivery of enterprise-grade AI solutions.
What is Langfuse? Langfuse is an open-source platform dedicated to LLM observability. It offers robust tracing and monitoring capabilities tailored for AI applications. Langfuse helps developers debug, analyze, and optimize their AI systems by providing detailed insights and integrating with a wide array of tools and frameworks through native integrations, OpenTelemetry, and dedicated SDKs.
Getting Started
Let’s walk through a practical example of using Semantic Kernel and integrating it with Langfuse for comprehensive tracing.
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Note: This notebook utilizes the Langfuse OTel Python SDK v3. For users of Python SDK v2, a previous version of this guide is available here.
%pip install langfuse openlit semantic-kernelStep 2: Configure Langfuse SDK
Next, set up your Langfuse API keys. You can get these keys by signing up for a free Langfuse Cloud account or by self-hosting Langfuse. These environment variables are essential for the Langfuse client to authenticate and send data to your Langfuse project.
import os
# Get keys for your project from the project settings page: https://cloud.langfuse.com
os.environ["LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY"] = "pk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY"] = "sk-lf-..."
os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇪🇺 EU region
# os.environ["LANGFUSE_HOST"] = "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com" # 🇺🇸 US region
# Your OpenAI key
os.environ["OPENAI_API_KEY"] = "sk-proj-..."
os.environ["OPENAI_CHAT_MODEL_ID"] = "gpt-4o"With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the Langfuse client. get_client() initializes the Langfuse client using the credentials provided in the environment variables.
from langfuse import get_client
langfuse = get_client()
# Verify connection
if langfuse.auth_check():
print("Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!")
else:
print("Authentication failed. Please check your credentials and host.")Langfuse client is authenticated and ready!
Step 3: Initialize OpenLit for Instrumentation
Now, we initialize the OpenLit instrumentation SDK. OpenLit automatically instruments Semantic Kernel and exports OpenTelemetry (OTel) spans to Langfuse.
import openlit
# Initialize OpenLIT instrumentation. The disable_batch flag is set to true to process traces immediately. Also set the langfuse tracer to use the langfuse tracer.
openlit.init(tracer=langfuse._otel_tracer, disable_batch=True)Step 4: Basic Semantic Kernel Application
Let’s create a straightforward Semantic Kernel application. In this example, an Assistant agent will answer a user’s question. This will serve as the foundation for demonstrating Langfuse tracing.
from semantic_kernel import Kernel
from semantic_kernel.connectors.ai.open_ai import OpenAIChatCompletion
kernel = Kernel()
kernel.add_service(
OpenAIChatCompletion(),
)from semantic_kernel.prompt_template import InputVariable, PromptTemplateConfig
prompt = """{{$input}}
Answer the question above.
"""
prompt_template_config = PromptTemplateConfig(
template=prompt,
name="summarize",
template_format="semantic-kernel",
input_variables=[
InputVariable(name="input", description="The user input", is_required=True),
]
)
summarize = kernel.add_function(
function_name="summarizeFunc",
plugin_name="summarizePlugin",
prompt_template_config=prompt_template_config,
)Step 5: Run the Application
With the Semantic Kernel application set up, let’s invoke it with a sample question and print the response. OpenLit will automatically capture this interaction and send the trace data to Langfuse.
input_text = "What is Langfuse?"
summary = await kernel.invoke(summarize, input=input_text)
print(summary)Step 6: View Traces in Langfuse
After executing the application, navigate to your Langfuse Trace Table. You will find detailed traces of the application’s execution, providing insights into the LLM calls, inputs, outputs, and performance metrics. Below is an example screenshot illustrating how a trace appears in Langfuse:
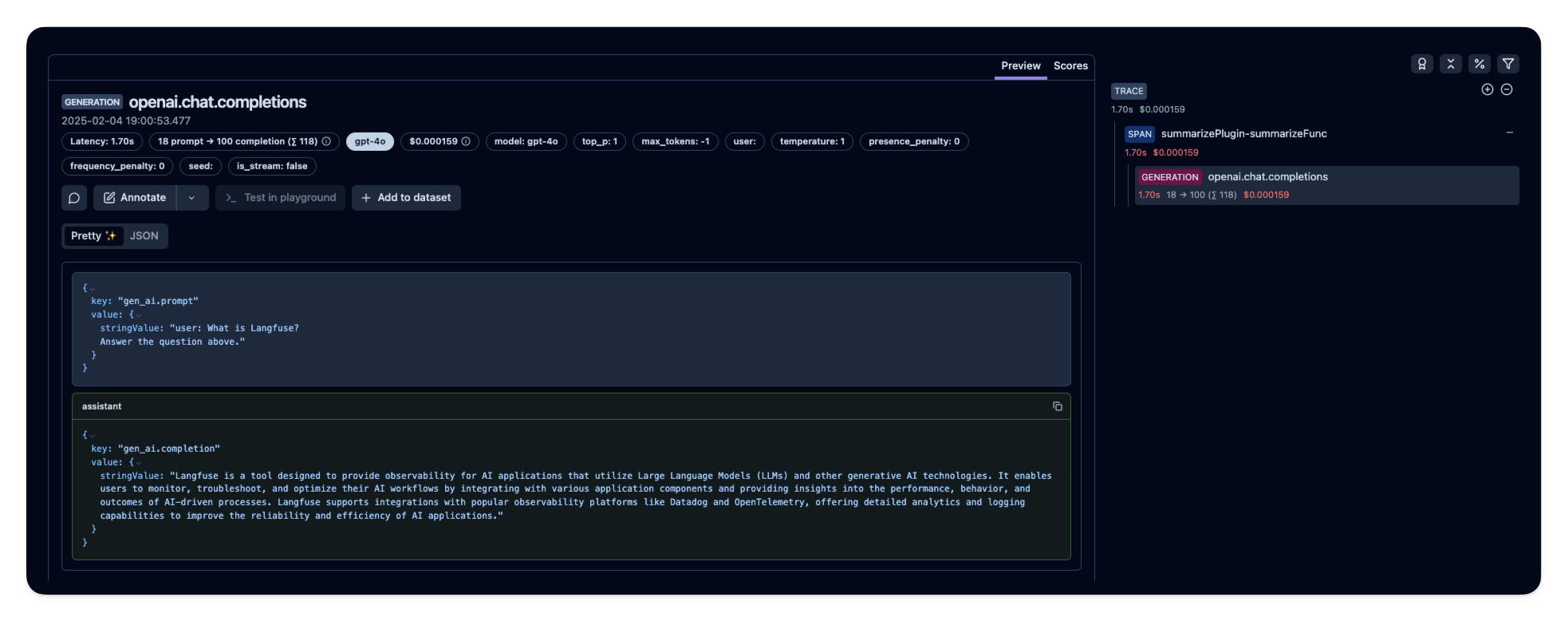
For a live example, you can explore this public trace: Langfuse Semantic Kernel Trace Example
Interoperability with the Python SDK
You can use this integration together with the Langfuse Python SDK to add additional attributes to the trace.
The @observe() decorator provides a convenient way to automatically wrap your instrumented code and add additional attributes to the trace.
from langfuse import observe, get_client
langfuse = get_client()
@observe()
def my_instrumented_function(input):
output = my_llm_call(input)
langfuse.update_current_trace(
input=input,
output=output,
user_id="user_123",
session_id="session_abc",
tags=["agent", "my-trace"],
metadata={"email": "[email protected]"},
version="1.0.0"
)
return outputLearn more about using the Decorator in the Python SDK docs.
Next Steps
Once you have instrumented your code, you can manage, evaluate and debug your application: