Cookbook: LiteLLM (Proxy) + Langfuse OpenAI Integration (JS/TS)


This notebook demonstrates how to use the following stack to experiment with 100+ LLMs from different providers without changing code:
- LiteLLM Proxy (GitHub): Standardizes 100+ model provider APIs on the OpenAI API schema.
- Langfuse OpenAI SDK Wrapper (JS/TS): Natively instruments calls to 100+ models via the OpenAI SDK.
- Langfuse: OSS LLM Observability, full overview here.
Note: This cookbook uses Deno.js for execution, which requires different syntax for importing packages and setting environment variables. For Node.js applications, the setup process is similar but uses standard
npmpackages andprocess.env.
Set Up Environment
Get your Langfuse API keys by signing up for Langfuse Cloud or self-hosting Langfuse. You’ll also need your OpenAI API key.
Note: This cookbook uses Deno.js for execution, which requires different syntax for importing packages and setting environment variables. For Node.js applications, the setup process is similar but uses standard
npmpackages andprocess.env.
// Langfuse authentication keys
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY", "pk-lf-***");
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY", "sk-lf-***");
// Langfuse host configuration
// For US data region, set this to "https://us.cloud.langfuse.com"
Deno.env.set("LANGFUSE_BASE_URL", "https://cloud.langfuse.com")
// Set environment variables using Deno-specific syntax
Deno.env.set("OPENAI_API_KEY", "sk-proj-***");With the environment variables set, we can now initialize the langfuseSpanProcessor which is passed to the main OpenTelemetry SDK that orchestrates tracing.
// Import required dependencies
import 'npm:dotenv/config';
import { NodeSDK } from "npm:@opentelemetry/sdk-node";
import { LangfuseSpanProcessor } from "npm:@langfuse/otel";
// Export the processor to be able to flush it later
// This is important for ensuring all spans are sent to Langfuse
export const langfuseSpanProcessor = new LangfuseSpanProcessor({
publicKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_PUBLIC_KEY!,
secretKey: process.env.LANGFUSE_SECRET_KEY!,
baseUrl: process.env.LANGFUSE_BASE_URL ?? 'https://cloud.langfuse.com', // Default to cloud if not specified
environment: process.env.NODE_ENV ?? 'development', // Default to development if not specified
});
// Initialize the OpenTelemetry SDK with our Langfuse processor
const sdk = new NodeSDK({
spanProcessors: [langfuseSpanProcessor],
});
// Start the SDK to begin collecting telemetry
// The warning about crypto module is expected in Deno and doesn't affect basic tracing functionality. Media upload features will be disabled, but all core tracing works normally
sdk.start();Setup Lite LLM Proxy
In this example, we’ll use llama3 via the Ollama on our local machine.
Steps
- Create a
litellm_config.yamlto configure which models are available (docs). We’ll use llama3 via Ollama in this example. - Ensure that you installed Ollama and have pulled the llama3 (8b) model:
ollama pull llama3 - Run the following cli command to start the proxy:
litellm --config litellm_config.yaml
The Lite LLM Proxy should be now running on http://0.0.0.0:4000
To verify the connection you can run litellm --test
Log single LLM Call via Langfuse OpenAI Wrapper
The Langfuse SDK offers a wrapper function around the OpenAI SDK, automatically logging all OpenAI calls as generations to Langfuse. We wrap the client for each call separately in order to be able to pass a name. For more details, please refer to our documentation.
import { OpenAI } from "npm:openai";
import { observeOpenAI } from "npm:@langfuse/openai";
const PROXY_URL = "http://0.0.0.0:4000";
const client = observeOpenAI(new OpenAI({baseURL: PROXY_URL}));
const systemPrompt = "You are a very accurate calculator. You output only the result of the calculation.";
const llamaCompletion = await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "ollama/llama3",
messages: [
{role: "system", content: systemPrompt},
{role: "user", content: "3 + 3 = "}
],
});
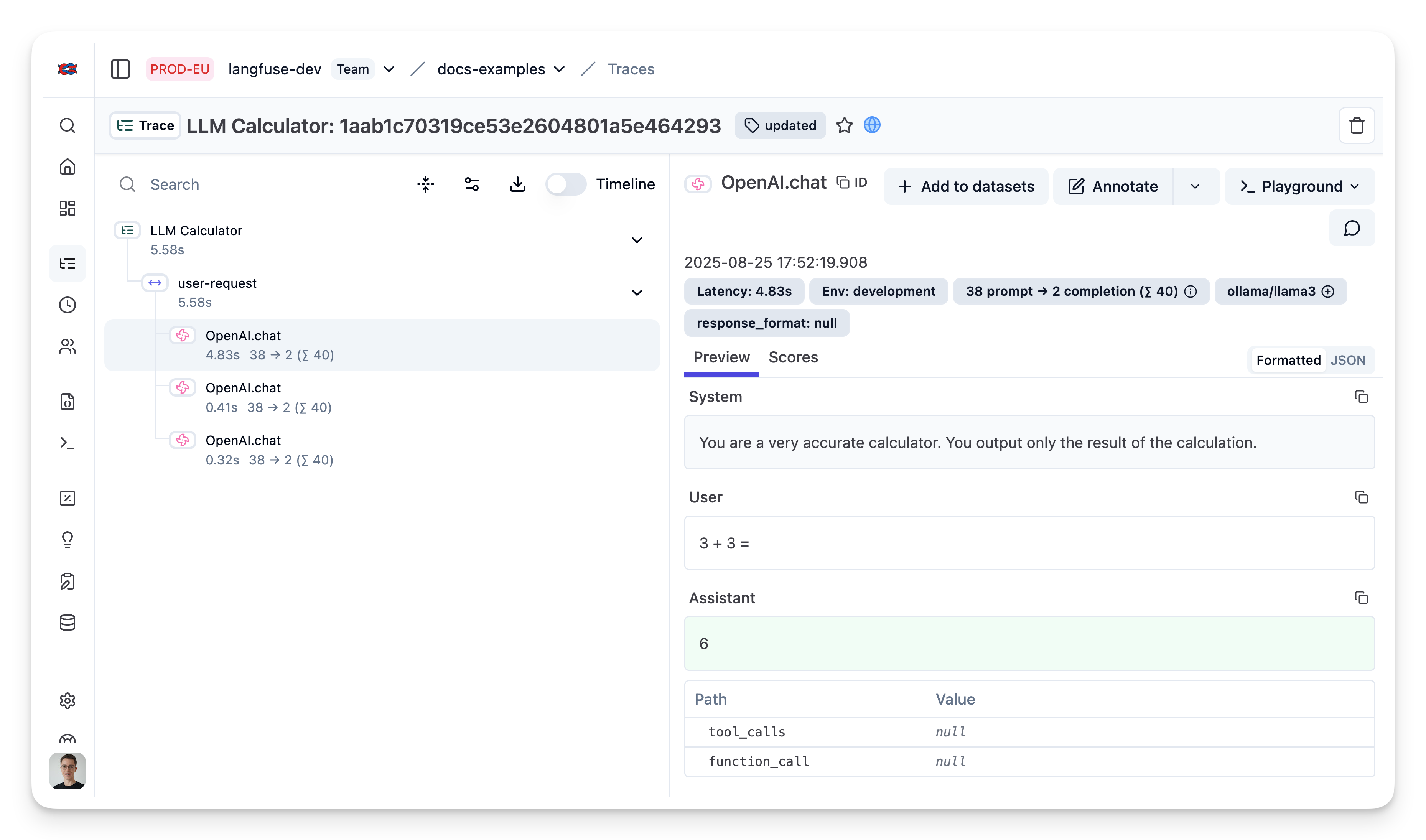
console.log(llamaCompletion.choices[0].message.content);6
Public trace in the Langfuse UI
Trace nested LLM Calls using Langfuse JS SDK
Use the context manager of the Langfuse TypeScript SDK to group multiple LiteLLM generations together and update the top level span.
import { startActiveObservation, startObservation, propagateAttributes } from "npm:@langfuse/tracing";
import { observeOpenAI } from "npm:@langfuse/openai";
const client = observeOpenAI(new OpenAI({baseURL: PROXY_URL}));
const systemPrompt = "You are a very accurate calculator. You output only the result of the calculation.";
await startActiveObservation("user-request", async (span) => {
await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "ollama/llama3",
messages: [
{role: "system", content: systemPrompt},
{role: "user", content: "3 + 3 = "}
],
});
await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "ollama/llama3",
messages: [
{role: "system", content: systemPrompt},
{role: "user", content: "1 - 1 = "}
],
});
await client.chat.completions.create({
model: "ollama/llama3",
messages: [
{role: "system", content: systemPrompt},
{role: "user", content: "2 + 3 = "}
],
});
// Propagate trace attributes
await propagateAttributes({
traceName: "LLM Calculator",
tags: ["updated"],
metadata: {"env": "development"},
release: "v0.0.2",
}, async () => {});
// Set input on the root observation
span.update({
input: systemPrompt,
});
});View traces in Langfuse
Learn more
Check out the docs to learn more about all components of this stack:
If you do not want to capture traces via the OpenAI SDK Wrapper, you can also directly log requests from the LiteLLM Proxy to Langfuse. For more details, refer to the LiteLLM Docs.